Intelligent transportation system is a hot topic among all civil engineering subjects that has gained popularity and many countries are successfully implementing it. With the rapidly exploding population, ITS has even become a mandatory technique in all countries. Here, we are going to read through the main components of the intelligent transportation system. We will swim through the benefits of intelligent transportation system in the middle, then to uses and challenges of ITS.
- What is intelligent transportation system?
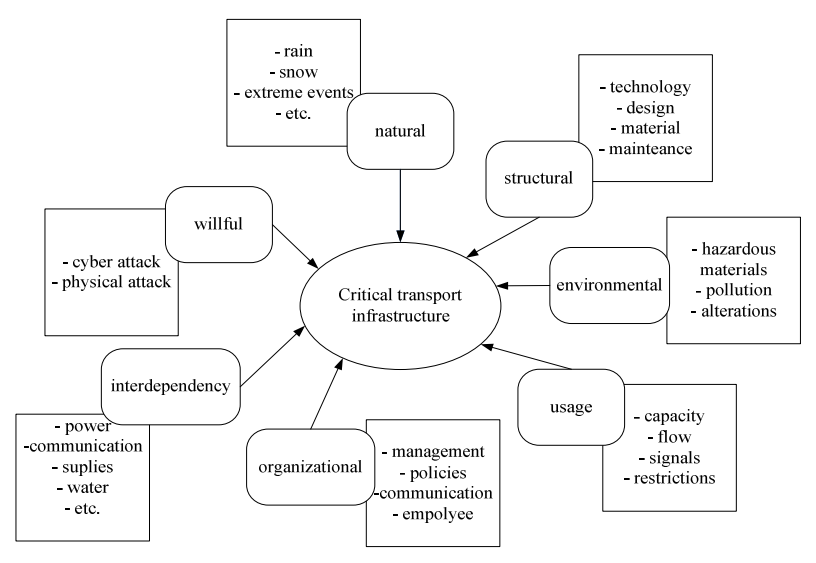
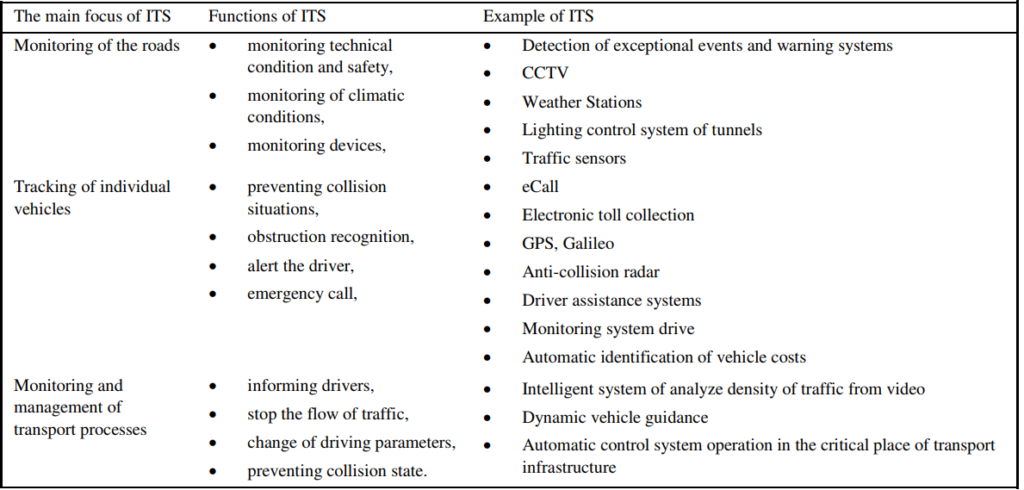
- Components of intelligent transportation system
- Benefits of intelligent transportation system
- Uses and challenges of intelligent transportation system
- 1. Use of cameras equipped with automatic number plate recognition(ANPR)
- 2. Speed violation recording cameras
- 3. Cameras for recording violations of passing through red-lights at intersections
- 4. Equipping the transportation system with GPS
- 5. Use of intelligent routing systems for public transportation passengers
- 6. Modern informative systems for offenders
What is intelligent transportation system?
What is Intelligent Transport System is the first step to dive in the topic. They are advanced applications which, aim to provide innovative services relating to different modes of transport and traffic management and enable various users to be better informed and make safer, more coordinated, and ‘smarter’ use of transport networks. In ITS the information and communication technologies are applied in the field of road transport, including infrastructure, vehicles and users, and in traffic management and mobility management, as well as for interfaces with other modes of transport.
Another answer to the question of what is Intelligent transportation system (ITS) is that, it is the application of sensing, analysis, control and communications technologies to ground transportation in order to improve safety, mobility and efficiency. ITS includes a wide range of applications that process and share information to ease congestion, improve traffic management, minimize environmental impact and increase the benefits of transportation to commercial users and the public in general.
Now, let me walk you through the main components of intelligent transportation system.
Related posts from vincivilworld
Components of intelligent transportation system
The main components of intelligent transportation system are,
1. Accurate tracking system
GPS enabled vehicles along with smartphone apps will help citizens to track buses and other vehicles.
2. Electronic timetables
Schedules of bus service should be updated in standard format which can be easily read by people and utilised by softwares.
3. Smart model to predict time of arrival
Transportation studies like that be conducted in IIT Madras, funded by Ministry of Urban Development. should be encouraged to obtain a robust algorithm to predict the arrival time of buses, which is what a citizen needs.
4. Standardisation by regulating authority
This is very important among all the components of intelligent transportation system. An authority should be set up which can standardise various components of the public transport and encourage the use of better and smart IT services in transport sector
5.Smart commuting
Latest information on traffic jams, accidents and ways for navigation
6. Mobile technology
App based technology, incentives for young technical entrepreneurs
7. Smart traffic control
Dynamic controls of traffic signals instead of current static control, automated system.
8. Scalability
The ITS should be easily applicable to 2nd tier cities so that problem of congestion doesn’t arise in the first place
9. Improved and better BRT system enacted with public participation
10. Installing CCTVs on traffic routes and in buses.
11. Creation of flyover and overbridges to eliminate need of traffic lights
12. Electronic payment of fare
13 Traveller’s advisory system like the use of advisory radio, SMS services, internet etc
14. Highway Management Systems: Use ramp metering techniques to measure and regulate by knowing the traffic entering or leaving the highway
15. Emergency Management Systems: To manage any unforeseen emergencies
16. Railroad Crossing: Gives signals about approaching rail junctions
17 Wireless communication System
18. Safe driving Support System
This includes,
a) Right turn collision prevention system
b) vehicle detection system
c) Pedestrian detection system
d) voice guidance
e) display warning
18. Electronic toll payment System
19. Computational technologie
20. Inductive loop detection and sensing technology
21.Freeway management.
Cool! Now how are these components of the intelligent transportation system benefiting transportation? Let’s see below.
Benefits of intelligent transportation system
The main benefits of intelligent transportation are as follows.
- Develop (and subsequently renew), a secure and effective revenue collection system – this has formed the backbone of the ITS
- Develop enhanced operations management capabilities to provide reliable services and deal with disruptions
- Provide communications for staff security
- Provide improved passenger information
- Obtain data for planning, resource optimisation and performance monitoring
- To assist the achievement of the quantity and quality of the service required in the service contract with the province of Florence
• To generate the trip logs, analysis and reporting required by the province of Florence under the service contract
• To manage the daily operations, on both normal and disrupted state
• To manage the driver vehicle handovers and shift-changes
• To provide the platform for real-time and other information to passengers
• To provide the platform for e-ticketing
• To identify vehicle faults and assist rapid response
• To support demand responsive transport and other non-standard mobility services
• To generate and manage data for post-event analysis, including running time analysis, scheduling, resource optimization, and incident investigation
So, I walked you through the important benefits of intelligent transportation system.
Its time to see the results now.
Uses and challenges of intelligent transportation system
1. Use of cameras equipped with automatic number plate recognition(ANPR)
Equip the intersections with traffic light crossing violations recording system and video surveillance cameras monitoring traffic flow
Advantages
Cameras are capable of fining any number of offending vehicles simultaneously
Challenges
- Drivers cover the number plate of their cars daily in order to not to be fined
- Some drivers who repeatedly pass specific passages try to destroy or damage the cameras and their equipment.
2. Speed violation recording cameras
Fixed cameras equipped with radar technology are assembled to identify and record speed violations
Advantage
Assured of getting fined through being caught on camera, drivers rarely attempt to drive over the speed limit
Challenges
- After identifying the locations where the cameras are installed, drivers may attempt to increase their speed in the distances between cameras, and this may cause many disturbances in traffic flow.
- Due to the weakness of technology, identifying motorcycles is not possible in this system
3. Cameras for recording violations of passing through red-lights at intersections
Cameras are assembled at intersections to record the red light running violations.
Advantages
A decrease in this kind of violation will have a direct effect in reducing car crashes and capital loss.
Challenges
- In many intersections, due to the low quality of crosswalks and zebra crossings, it is really hard to determine a threshold running from which enables the driver to be known as an offender
- As in many intersections, turning left or right is not legally forbidden, it is really a hard job to distinguish the vehicles doing so from the violators.
4. Equipping the transportation system with GPS
Position of the buses and the approximate arrival time of buses to stations can be calculated those who are speeding or using unauthorized routes can be identified
Advantages
- Reduction of dangerous high speed of buses
- Decreasing of delay time of journey
Challenges
- Some drivers try to deactivate the GPS before attempting violation. They cover the GPS with aluminum foil to make it disconnected from the center.
- Due to the need for a GPRS platform for sending the information to the center, using this system in Tehran is very expensive.
- Due to the low average educational level of drivers and users of public transportation services, the relevant systematic training for using this system will be needed.
5. Use of intelligent routing systems for public transportation passengers
Passenger can receive information about the journey duration and the best manner of navigation after determining the origin and destination and also specifying the desired transportation mode such as metro, taxi, bus or walking
Advantages
Decrease in delay of journeys and an increase in productivity.
6. Modern informative systems for offenders
All fine notifications and notices for a technical test will be informed to the offenders via SMS
Advantages
- Deliver the fine notifications to the offenders, omitting the process of printing and stuffing envelopes with fine notification
- Informing all offenders of their violations in an online manner, and creating a cohesive database of the offenders.
Challenges
- As the telecommunications system and necessary infrastructure have not been completely developed, some problems in sending the SMS to offenders have been occasionally observed.
- Informative limitations such as length of words in SMS.
That’s it about ITS.
Continue learning!
MUST READ: Basic of civil engineering; Simple and in-depth guide