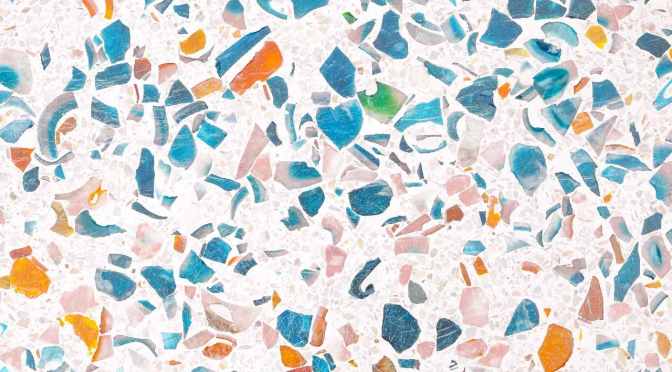
Terrazzo flooring is a stunning and durable option for residential and commercial spaces. It combines marble, quartz, granite, or glass chips with a cement or epoxy binder to create a unique and elegant surface. Terrazzo floors offer endless design possibilities, with various colours, patterns, and finishes available. With its timeless appeal, durability, and low maintenance, terrazzo flooring is a popular choice for those seeking a beautiful, long-lasting solution.
Terrazzo flooring incorporates a mix of materials such as marble, quartz, granite, or glass chips, creating a visually striking and versatile floor. Its popularity stems from its exceptional durability, easy maintenance, and ability to be customized to suit any aesthetic, making it a preferred choice for architects and designers.
- Terrazzo flooring – Types and ingredients
- Advantages of Epoxy Terrazzo Flooring over Cementitious Terrazzo Floor
- Advantages of Terrazzo Flooring
- Conclusion
Terrazzo flooring – Types and ingredients
Terrazzo flooring comes in various types, each offering unique characteristics and aesthetic appeal. From traditional and Venetian to epoxy and rustic, here are some common terrazzo flooring types to explore.
- Traditional Terrazzo: This type uses a cement binder mixed with marble, quartz, or other aggregates. They provide a classic and timeless look.
- Epoxy Terrazzo: Instead of cement, epoxy resin is used as the binder. Epoxy terrazzo offers greater design flexibility, durability, and a smoother finish.
- Venetian Terrazzo: Originating from Italy, Venetian Terrazzo features a polished finish and intricate patterns. These patterns are created by embedding various colourful marble chips in a cement binder.
- Rustic Terrazzo: This type showcases a more textured and natural appearance. They often incorporate larger aggregate chips for a rustic, earthy aesthetic.
- Aggregate Terrazzo: It consists of a single type of aggregate, such as recycled glass or marble chips, mixed with a binder, resulting in a uniform and minimalist design.
- Monolithic Terrazzo: This refers to terrazzo that is poured on-site without any precast or separate installation. It offers seamless, continuous flooring with endless design possibilities.
These are just a few examples, as terrazzo flooring can be customized to meet specific design preferences. This allows for an extensive range of variations and combinations.
Epoxy Terrazzo Flooring
Epoxy terrazzo flooring is a popular choice known for its durability, versatility, and seamless finish. It utilizes an epoxy resin binder mixed with aggregates like marble, quartz, or glass chips, creating a highly customizable surface. Epoxy terrazzo is resistant to stains, chemicals, and moisture, making it ideal for high-traffic areas and contemporary design schemes.
Advantages and applications of Epoxy terrazzo flooring
Epoxy terrazzo floor offers several advantages and finds wide applications in various settings. Its seamless finish eliminates grout lines, making maintenance easier and preventing dirt and bacteria build-up. It is highly durable, resistant to stains, chemicals, and impact. Epoxy terrazzo’s versatility allows for limitless design possibilities, including intricate patterns and vibrant colours. It is commonly used in commercial spaces like airports, hospitals, schools, and retail stores. They are also used in residential projects, due to its aesthetic appeal and long-lasting performance.
Traditional terrazzo or cementitious Terrazzo Flooring
Cementitious terrazzo flooring comes in various types, each offering unique characteristics. Common types include Venetian terrazzo, which features intricate patterns and colourful marble chips; rustic terrazzo, known for its textured and natural appearance; and aggregate terrazzo, using a single type of aggregate like recycled glass or marble chips for a minimalist design. These variations allow for a wide range of aesthetic options to suit different preferences.
Monolithic terrazzo refers to terrazzo flooring that is poured on-site without separate installation or precast elements. It provides a seamless and continuous surface, allowing for unlimited design possibilities and a visually cohesive look.
Advantages of Epoxy Terrazzo Flooring over Cementitious Terrazzo Floor
Here is a comparison between epoxy terrazzo flooring and cementitious terrazzo flooring:
- Durability: Epoxy terrazzo has superior chemical and stain resistance, making it more resistant to wear and tear compared to cementitious terrazzo.
- Design Versatility: Epoxy terrazzo offers a wider range of design possibilities, including vibrant colours, intricate patterns, and decorative effects, whereas cementitious terrazzo has more limited options.
- Seamless Finish: Epoxy terrazzo provides a seamless finish without grout lines, making it easier to clean and maintain compared to cementitious terrazzo.
- Installation Time: Epoxy terrazzo has a faster installation process, as it requires less curing time compared to cementitious terrazzo.
- Cost: Epoxy terrazzo tends to be more cost-effective than cementitious terrazzo, depending on the complexity of the design and project size.
It’s important to consider specific project requirements and design preferences when choosing between epoxy terrazzo and cementitious terrazzo flooring.
Advantages of Terrazzo Flooring
Terrazzo floor offers several advantages over other popular flooring choices:
- Durability: Terrazzo is highly durable and long-lasting, surpassing materials like laminate, vinyl, or carpet.
- Design Options: Terrazzo provides endless design possibilities with customizable colours, patterns, and aggregates, unlike the limited options of hardwood or tile.
- Low Maintenance: Terrazzo requires minimal maintenance, with easy cleaning and resistance to stains and scratches, unlike carpet or natural stone.
- Sustainability: Terrazzo is eco-friendly, often using recycled materials and reducing waste, making it a greener choice compared to some floor options.
- Versatility: Terrazzo can be used both indoors and outdoors, accommodating various spaces, while materials like carpet or hardwood may have limited outdoor usage.
- Allergen Reduction: Unlike carpet, terrazzo does not trap allergens and is hypoallergenic, promoting a healthier indoor environment.
- Longevity: Terrazzo has a long lifespan, exceeding the durability of materials like laminate or vinyl, offering a cost-effective solution over time.
Terrazzo’s unique blend of durability, aesthetic appeal, low maintenance, and sustainability make it stand out among popular flooring choices.
Conclusion
Terrazzo flooring is a versatile, durable, and visually striking option for both residential and commercial spaces. With its timeless appeal and low maintenance, terrazzo floor offers a long-lasting and elegant solution for any design aesthetic.