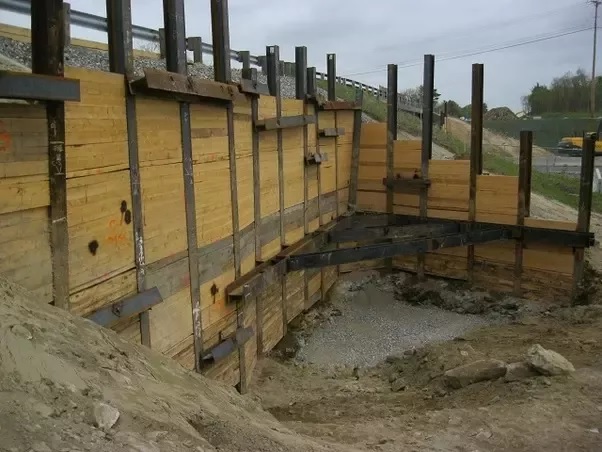
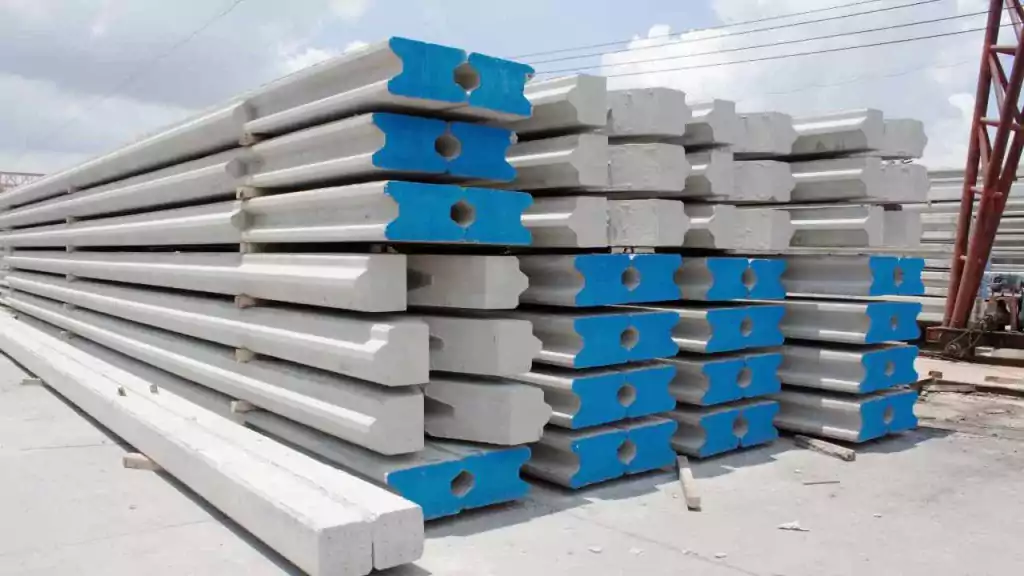
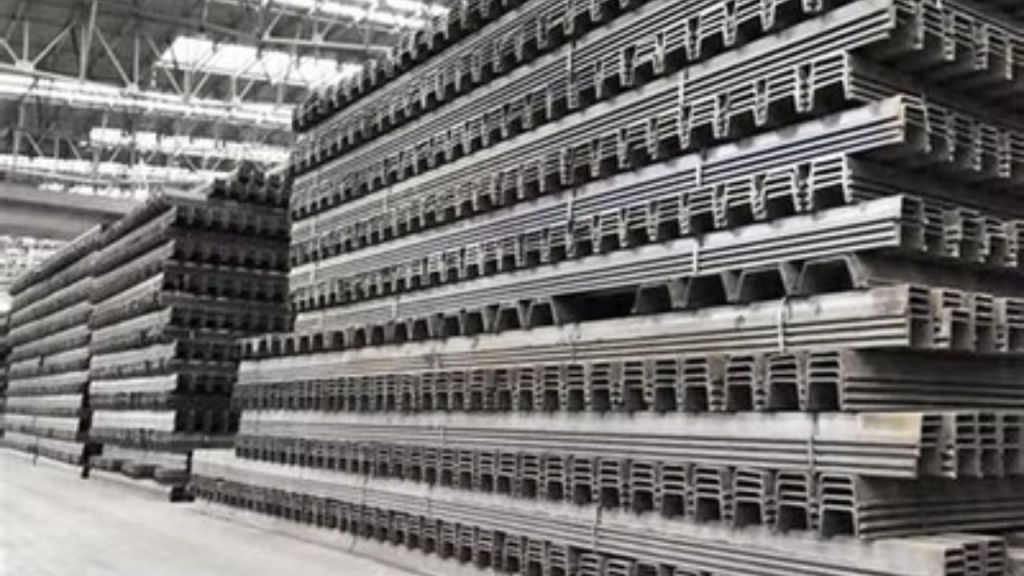
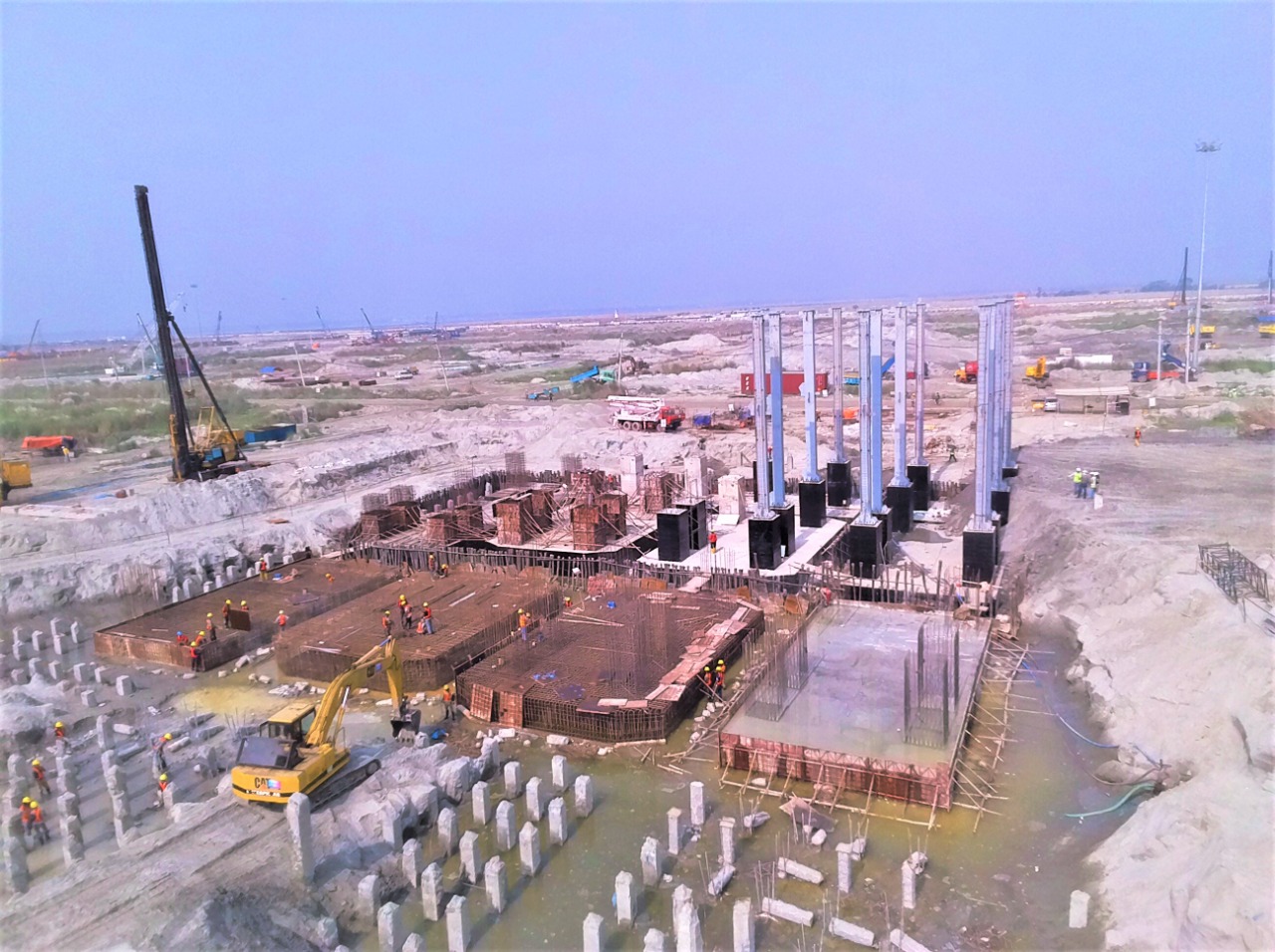
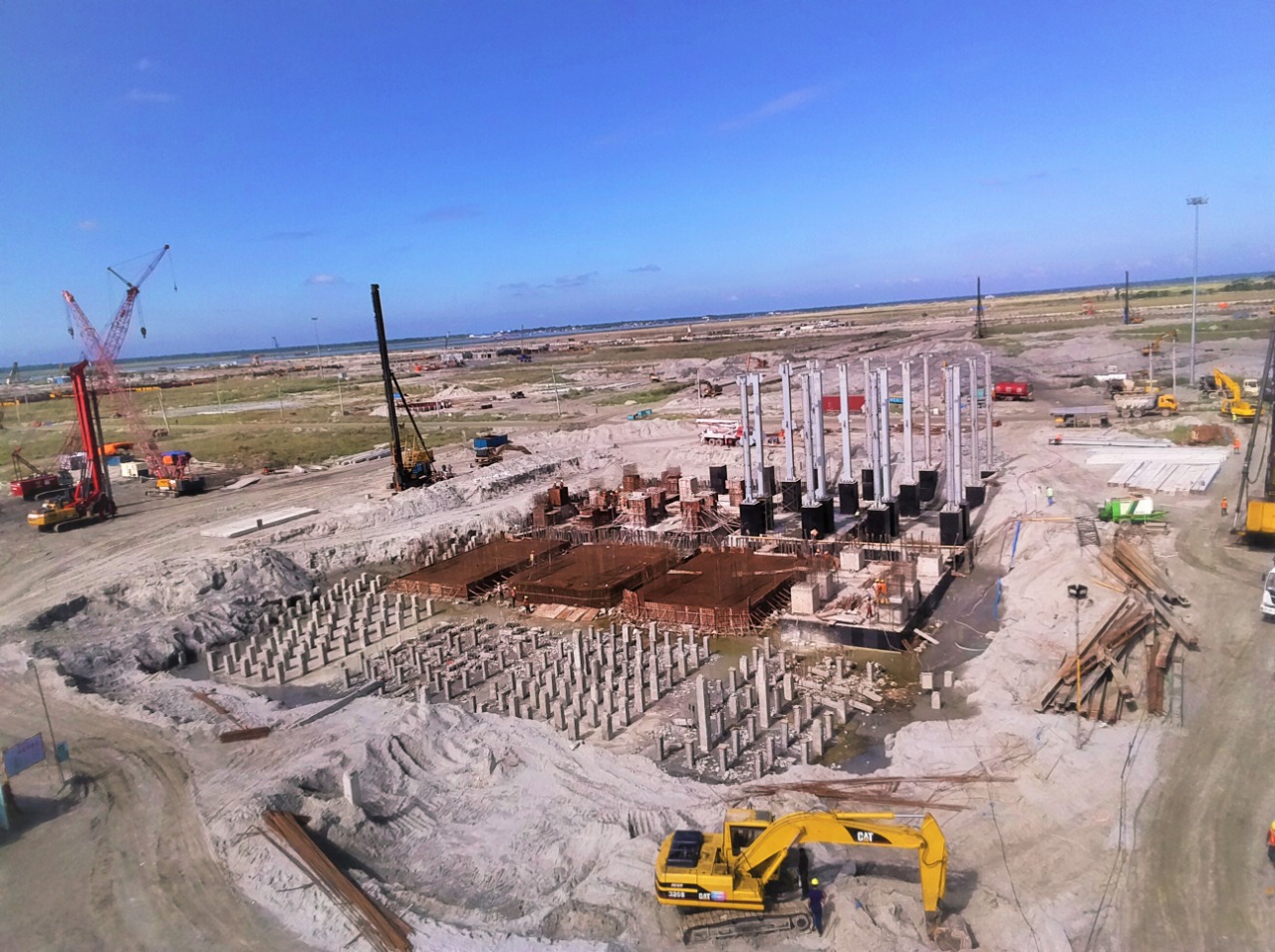
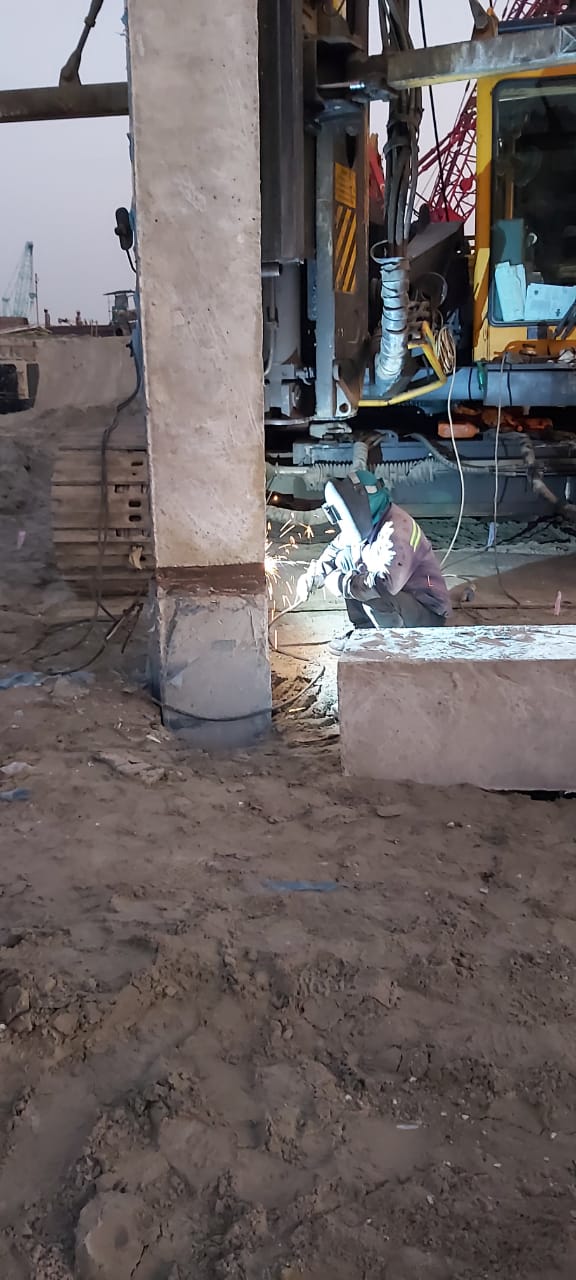
Sheet piles are essential components in construction and civil engineering. They are used in various applications, including retaining walls and foundations. The process of sheet piling involves driving long, vertical sections of sheet piles into the ground. This technique is crucial for creating a stable sheet pile foundation. There are different types of sheet piling, each designed for specific conditions and uses. Shore piling is another method related to sheet piling, primarily used for waterfront construction. To achieve successful project outcomes, it is important to understand sheet piling work. Familiarity with the types of sheet piling available is also beneficial in various construction scenarios.
In this article, we will explore the various types of sheet piling and their applications in construction. We will discuss the installation process of sheet piling work and the advantages of using a sheet pile foundation. Additionally, we’ll cover shore piling and how these techniques contribute to structural stability and safety in diverse projects.
- What is a sheet pile ?
- Sheet piling method
- Sheet piles – Applications
- Advantages of sheet pile
- Sheet piling types
- Conclusion
What is a sheet pile ?
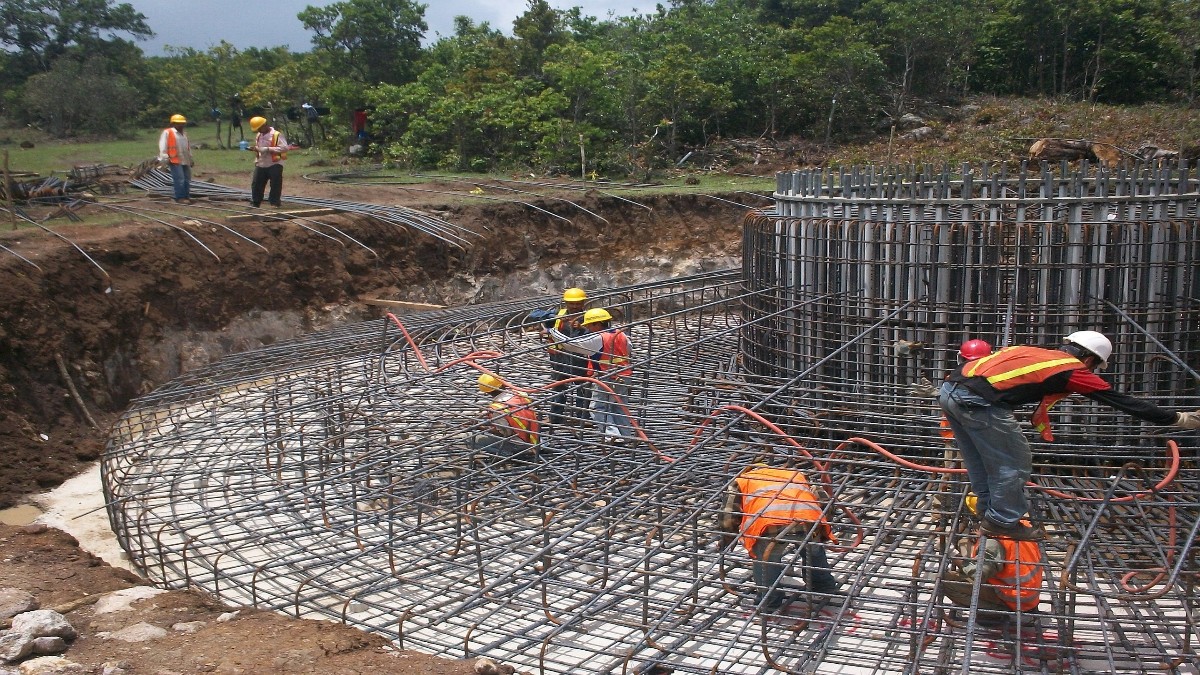
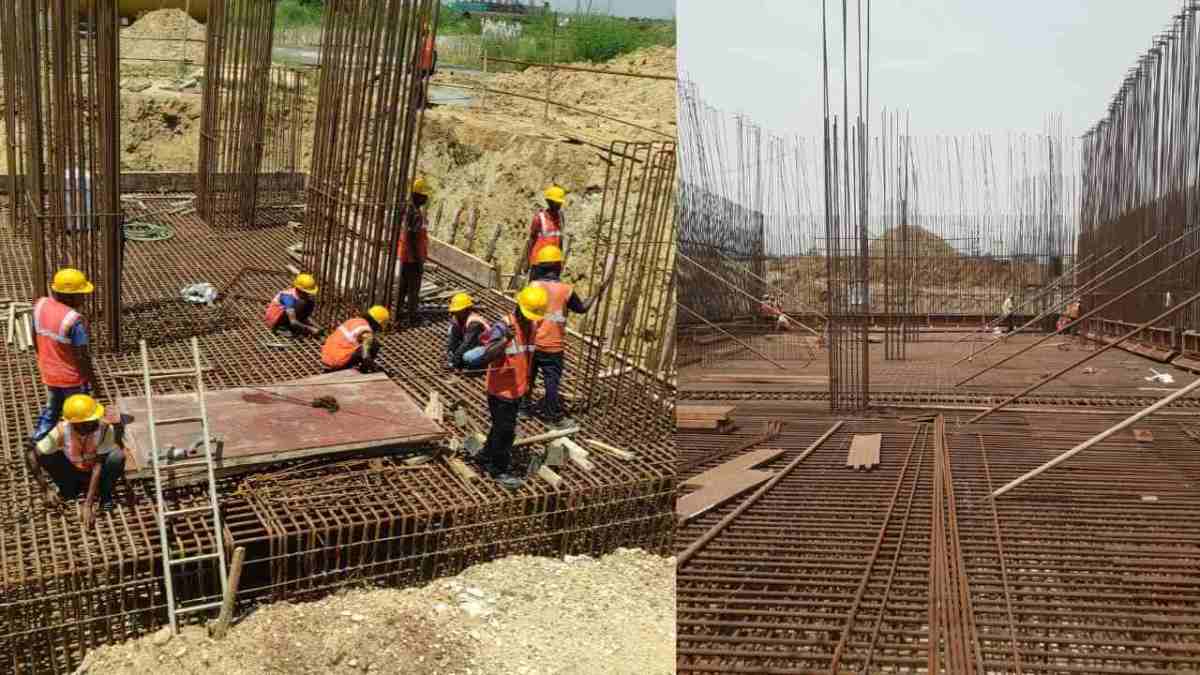
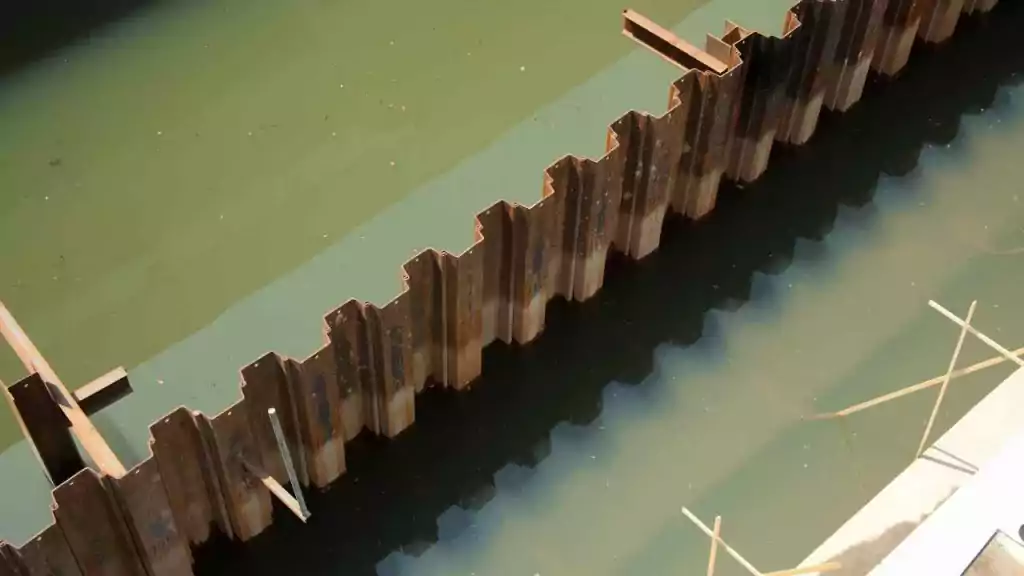
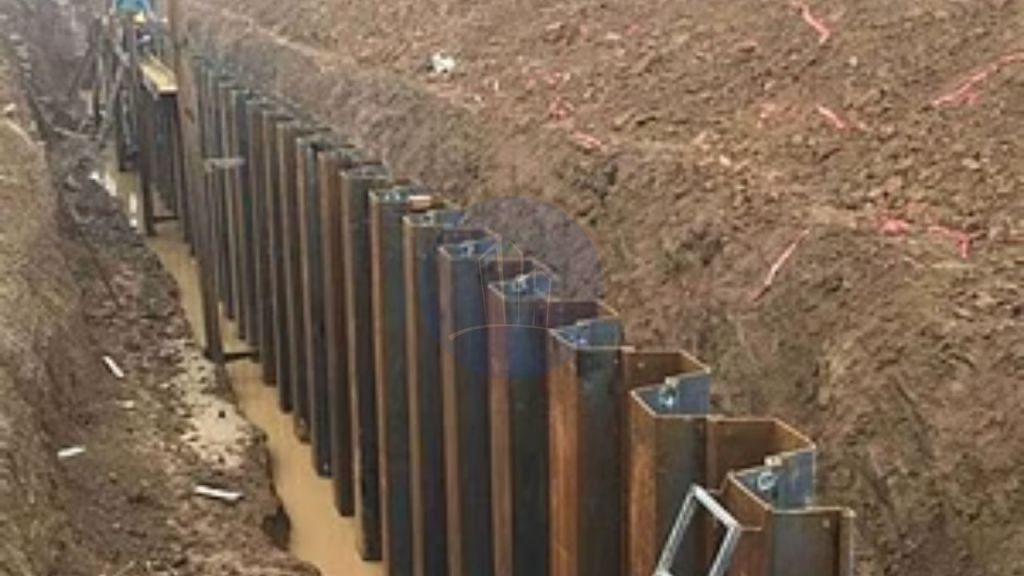
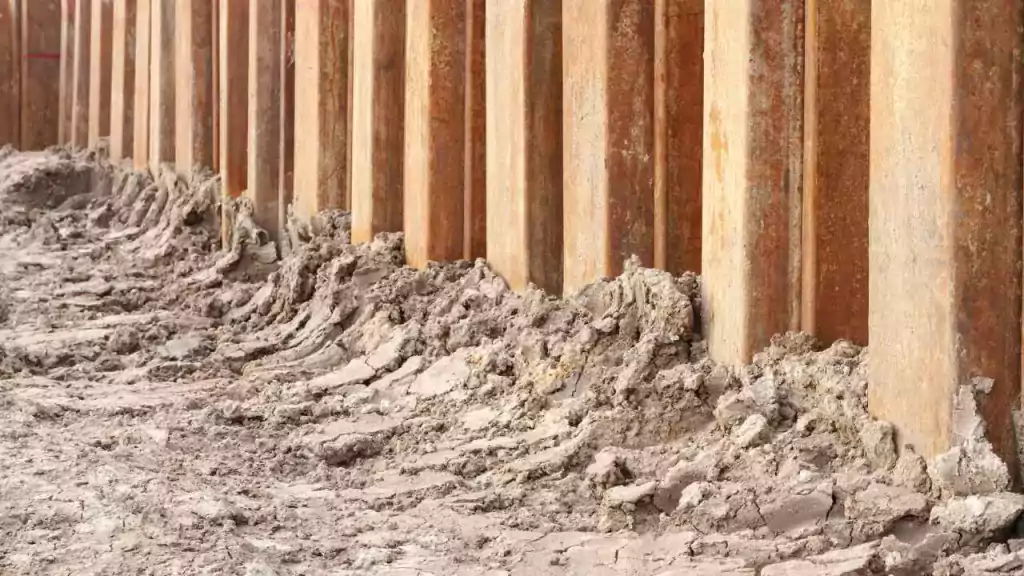
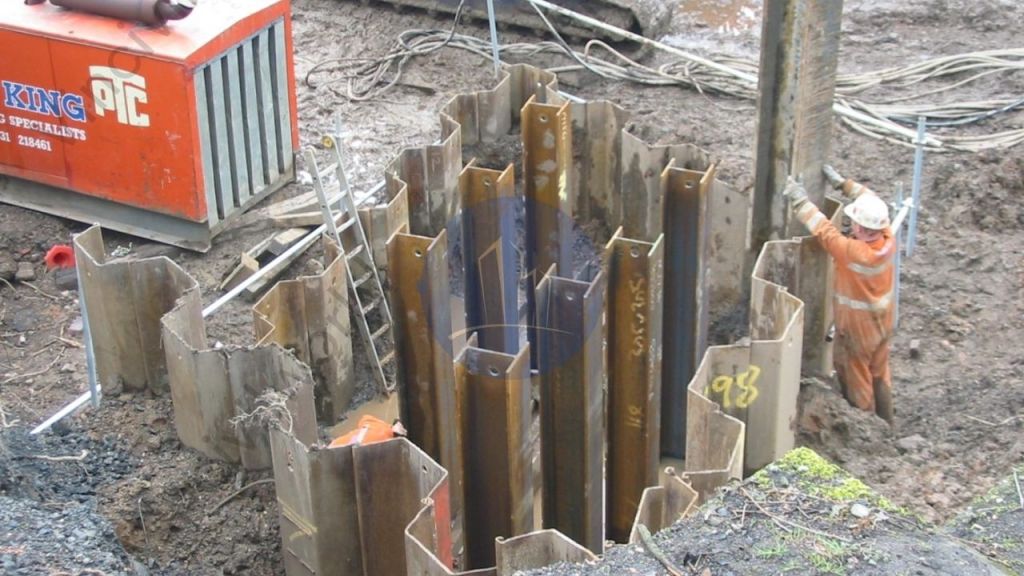
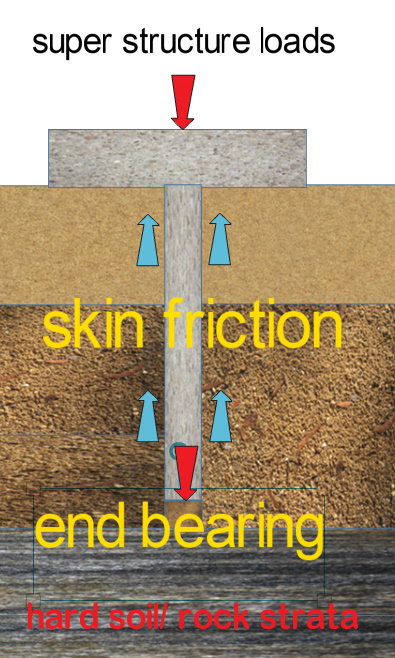
A sheet pile is a type of driven pile that uses sections of sheet materials with interlocking edges. We generally install Sheet piles for lateral earth retention, excavation support, and shoreline protection operations. They are typically made of steel, but can also be made of vinyl, wood, or aluminum. Sheet piles are installed in sequence to the design depth along the excavation perimeter or seawall alignment. The interlocking sheet piles provide a wall for permanent or temporary lateral earth support with little groundwater inflow. We use Anchors strategically to provide lateral support Anchors.
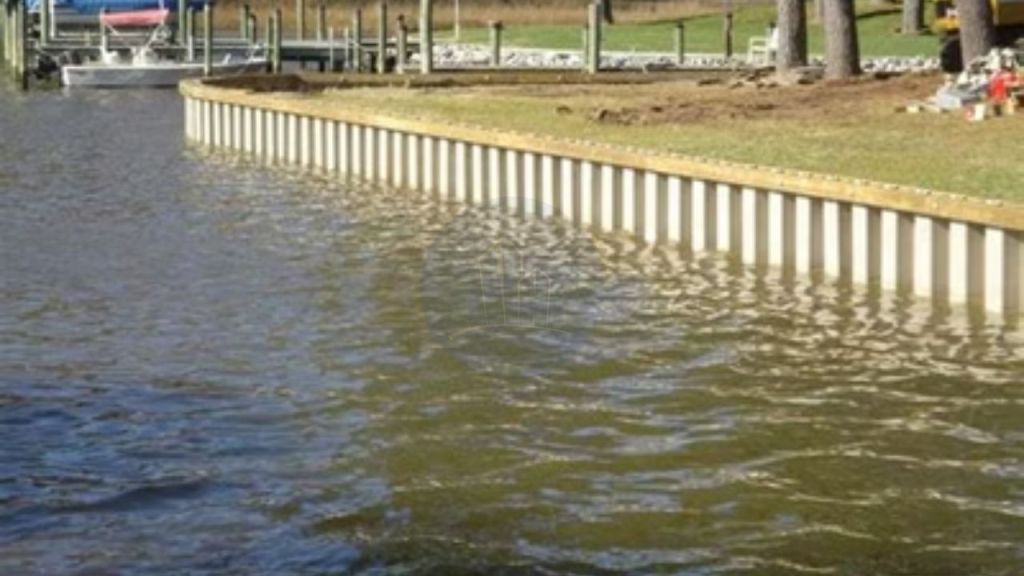
We frequently use Sheet piles for seawalls, retaining walls, land reclamation, and underground constructions. Underground constructions include parking garages, and basements, in marine locations for riverbank protection, seawalls, cofferdams, and so on.
Sheet piling method
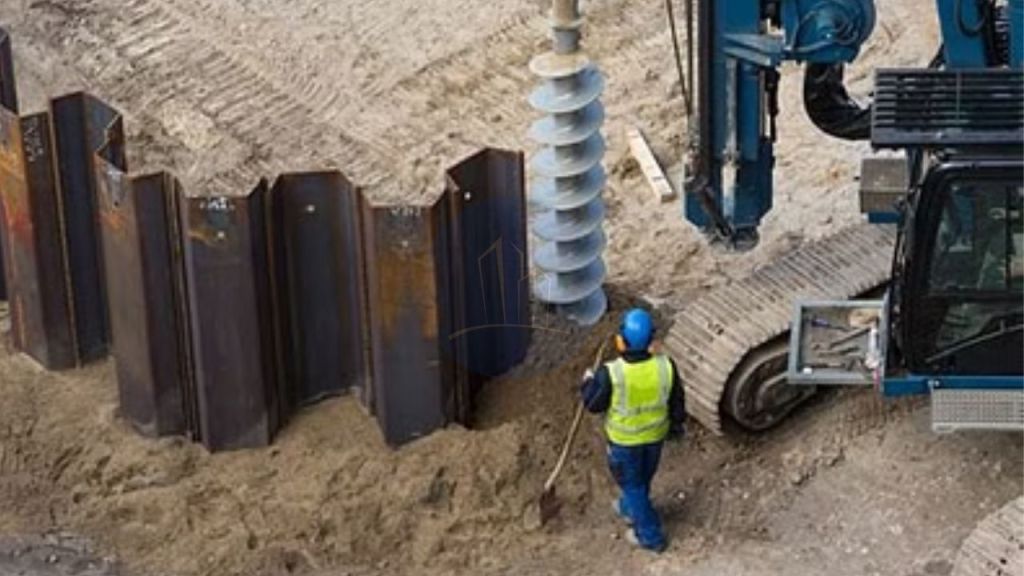
Sheet piles can be temporary or permanent. Permanent steel sheet pile design demands a long service life. Often we install Sheet piles using vibratory hammers. If the earth is too hard or dense, we perform the installation with an impact hammer. Hot-rolling and cold-forming are the two major methods for creating sheet piles. Manufacturing of Hot rolled piles takes place at high temperatures, and the interlocks appear to be stronger and more durable.
Related contents from vincivilworld
Sheet piles are installed by driving them into the ground with an impact hammer or vibratory driver. We connect them to one another by using a number of interlocking mechanisms. This includes tongue-and-groove, hook-and-grip, and clutch-bolt connections. Sheet piles, once erected, form a continuous barrier. This barrier resists lateral pressure from soil or water. It prevents soil erosion, landslides, and other soil failures.
Sheet piles – Applications
Piles find frequent utilization in the following construction projects:
Retaining walls
Sheet piles help to construct retaining walls that hold back soil or water while also providing lateral support for excavations.
Coastal protection:
Sheet piling can protect coastal areas from erosion, waves, and storm surges. They can also be used to construct breakwaters and jetties.
Cofferdams
Sheet piles are used to build cofferdams. These are transient obstructions in water. They facilitate the construction of piers, bridges, or other water-based constructions.
Underground structures
We use Sheet piles to construct underground constructions such as basements or underground parking garages. They support the lateral structure and restrict soil or water intrusion.
Sheet piles have various advantages, including their versatility, ease of installation, and durability. Moreover, they offer an affordable option for projects that need lateral earth support. However, adequate design and installation are essential for guaranteeing the sheet pile wall’s stability and safety.
Advantages of sheet pile
Sheet piles provide several advantages in construction projects that require lateral earth support. Following are some of the key benefits of sheet piles:
- Versatility: Sheet piles find applications in a variety of construction projects, including retaining walls, shoreline protection, cofferdams, and underground structures.
- Speed of installation: Sheet piles are installed quickly and efficiently. We use impact hammers or vibratory drivers for this. These methods can reduce project timelines and construction costs.
- Durability: Sheet piles are made from steel or other durable materials. They can withstand harsh environmental conditions, including exposure to water, corrosion, and extreme temperatures. This makes them highly durable.
- Cost-effectiveness: Sheet piles generally prove to be a more affordable alternative to other types of foundation systems. They are ideal for projects requiring lateral earth support since they need less excavation and backfilling.
- Minimal disturbance: Sheet pile installation creates minimal disturbance to the surrounding soil and structures. We drive the piles into the ground without the need for excavation or other site preparation.
- Reusability: Sheet piles offer easy removal and reuse in other projects, making them a sustainable and Eco-friendly alternative.
- We use sheet piles for temporary and permanent structures. They are available in a wide range of lengths, sizes, and steel options.
- We can install Sheet piles rapidly using silent and vibration-free methods. The installation is easier and faster than secant walls.
- We can construct Cofferdams in almost any desired shape. Provide a close-fitting joint to form an effective water seal. Joints are designed to withstand the high pressure necessary for them to be placed in place. A little maintenance is needed above and underwater
Sheet piling types
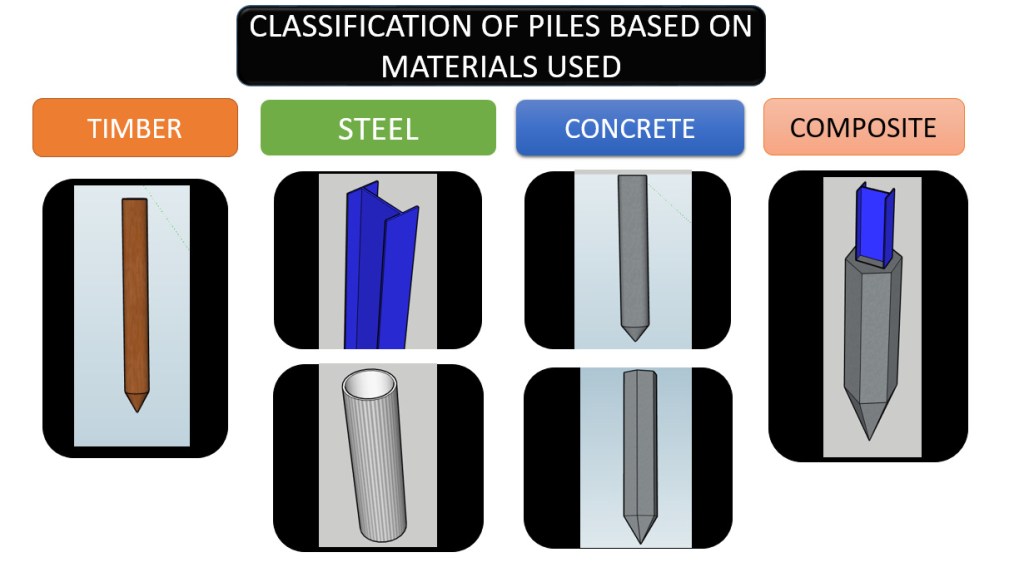
Sheet piles are broadly classified as follows based on the material used for driving.
- Steel sheet pile
- Vinyl sheet pile
- Wooden sheet pile
- Concrete sheet pile
- Composite sheet piles
- Cellular sheet pile
- Cellular sheet pile
- Cold-formed sheet pile
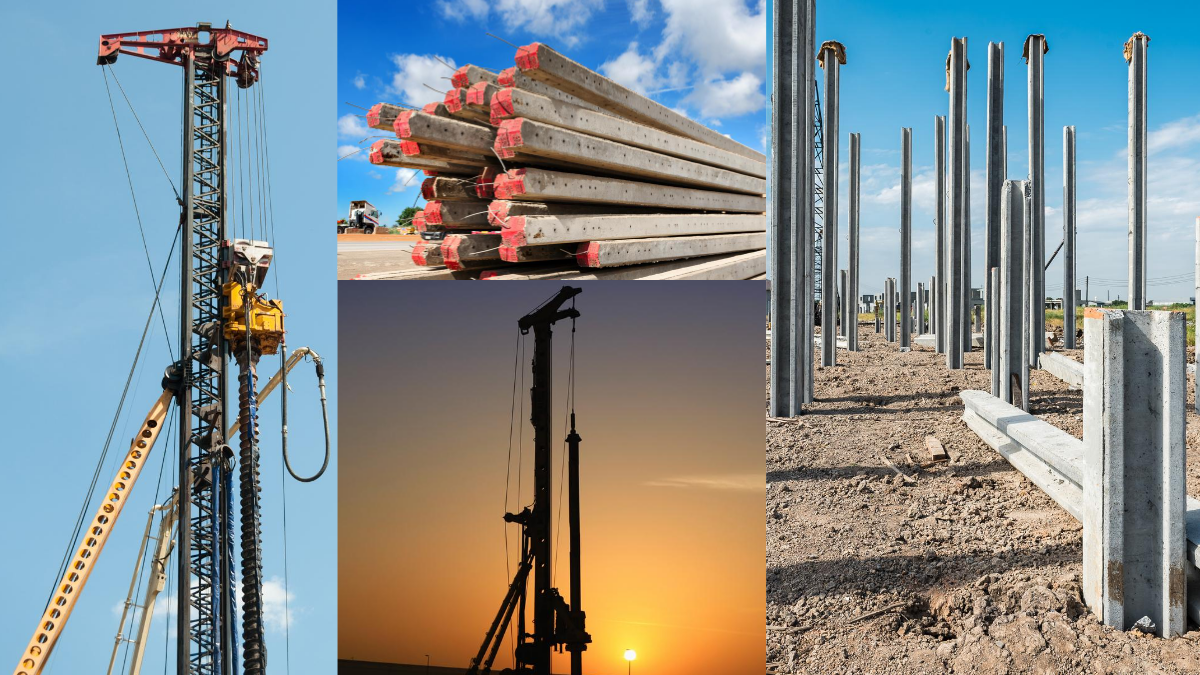
Steel Sheet piles
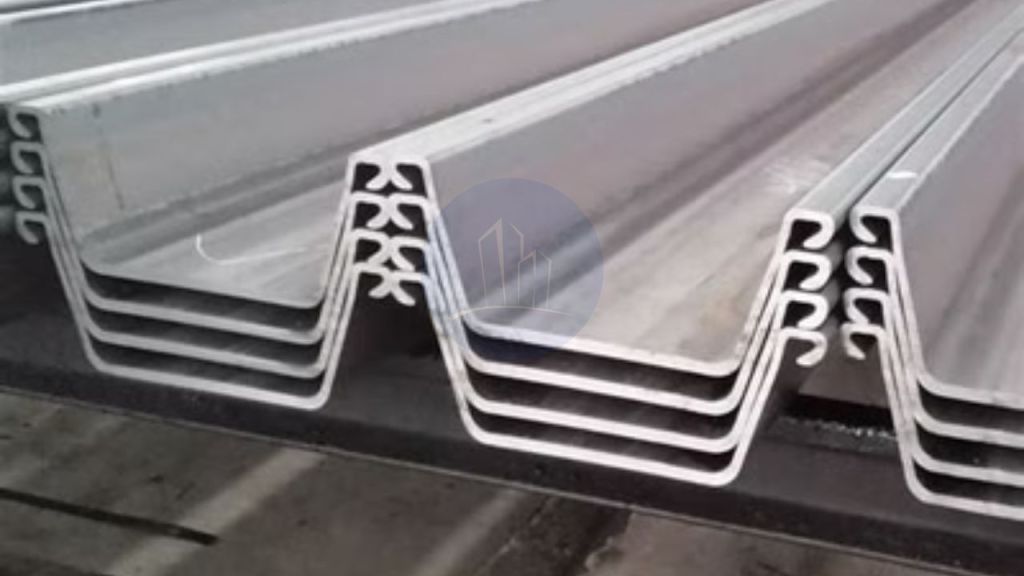
Steel sheet piles are long and thin sections of steel. They are driven into the ground to construct a retaining wall or a barrier. Steel is the most popular material for sheet piles. We can lengthen it either by welding or bolting. Steel has great water tightness and good resistance to severe driving stresses. They find extensive applications in civil engineering and construction projects. These applications include providing structural support for excavations, bridges, highways, and other structures.
Steel sheet piles are primarily made of hot-rolled steel and are available in a variety of shapes and sizes. We can link them together to form a continuous wall. This wall acts as a strong barrier against the soil or water pressure. Steel sheet piles should endure heavy loads and give structural stability. Corrosion prevention techniques including coating and cathodic protection help increase the durability of steel sheet pile.
We frequently use Steel sheet piles in foundation work and deep excavations. They offer high resistance to lateral stresses. They also enable quick and simple installation. They are an Eco-friendly option for temporary constructions because we can recycle them.
Overall, steel sheet piles are a versatile and cost-effective solution for a wide range of civil engineering and construction projects.
There are four basic forms of steel sheet piles, Normal sections, Straight web sections, Box sections and Composite sections.
Vinyl sheet pile
A vinyl sheet pile is a form of plastic sheet pile. It finds applications in civil engineering and construction projects. These applications include seawalls, bulkheads, flood walls, and retaining walls. Vinyl sheet pile is primarily made of polyvinyl chloride (PVC). PVC is a lightweight and long-lasting polymer. It is resistant to corrosion, chemicals, and weathering. Vinyl sheet pile is becoming more common in construction projects. This is due to its minimal maintenance requirements. Its simplicity of installation and long-term durability also contribute to its popularity. Vinyl sheet pile does not require frequent maintenance or coating. Unlike traditional materials such as wood, steel, or concrete, this makes it a more cost-effective alternative in the long run.
Vinyl sheet pile is also environmentally friendly because it is reusable and does not leak dangerous chemicals into the soil or water. Because of its lightweight qualities, it is simple to transport and install, necessitating minimal use of heavy machinery and labour. Overall, vinyl sheet pile is a versatile and cost-effective solution for a variety of construction and civil engineering projects. Its durability, low maintenance requirements, and environmental benefits make it an appealing choice for contractors and engineers.
An effective alternative to steel sheet piling for bulkheads, seawalls and cutoff walls. They are also superior to alternative materials like concrete and wood. The main advantage of vinyl sheet piles is the superior corrosion resistance when exposed to seawater, where no oxidation occurs.
Vinyl sheet piles are lightweight and resistant to corrosion and chemical damage. They are often used in projects where environmental impact is a concern.
Wooden sheet pile
A wooden sheet pile is a type of retaining system comprising timber planks or boards. We commonly employ them in construction and civil engineering projects with a requirement for a retaining wall, either temporary or permanent. Hardwood sheet piles are a more environmentally friendly and long-lasting alternative to steel or concrete sheet piles. and they are widely utilised in places where environmental impact is a concern. In excavation work, we utilise them for braced sheeting and temporary structures. It must have some sort of preservative treatment for its utilisation in permanent structures above the water table. Even after treatment with a preservative, a timber sheet pile has limited life. Timber sheet piles are bonded using tongue and groove connections.
Features of wooden piles
Timber piles are not suitable in strata that contain gravel and boulders. Hardwood sheet piles are ideal for shallow excavations and we frequently utilise them in building projects where noise and vibration are a concern. They are lightweight and easy to handle, making them a popular choice for jobs requiring speedy installation. In comparison to other retaining wall materials, wooden sheet piles are also more affordable. Yet, there are significant drawbacks to using hardwood sheet piles. They are not as robust as steel or concrete sheet piles and require frequent maintenance to prevent rot and insect infestation. They may also be prone to warping and deformation if exposed to dampness for a lengthy period of time.
Hardwood sheet piles may not be suited for usage in places with high water tables or salinity in the soil, as these variables might accelerate the decomposition of the timber. Overall, hardwood sheet piles are an efficient and environmentally friendly option for small-scale building projects and temporary retaining walls. Yet, their durability and susceptibility to deterioration and warping make them unsuitable for long-term or large-scale applications.
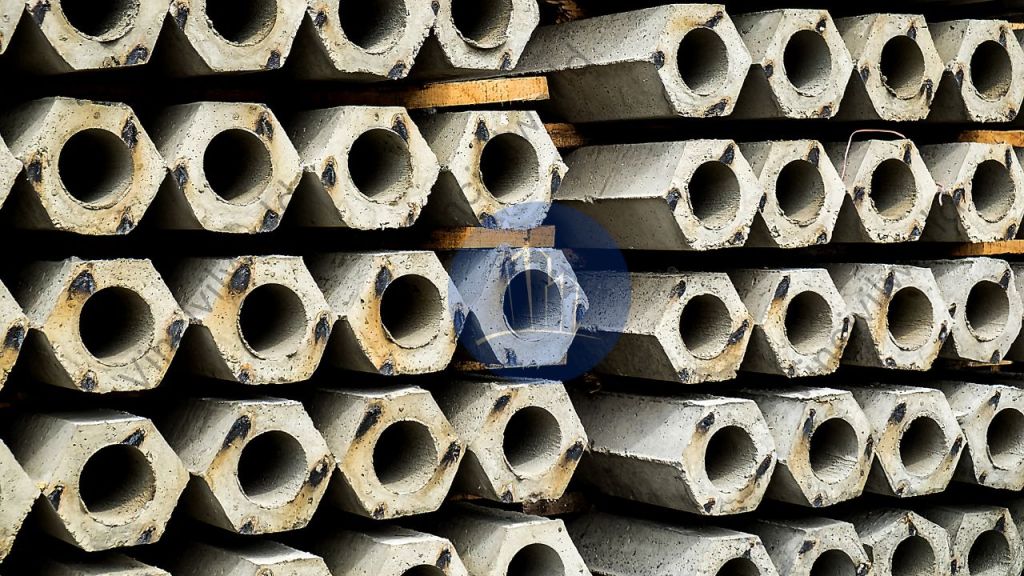
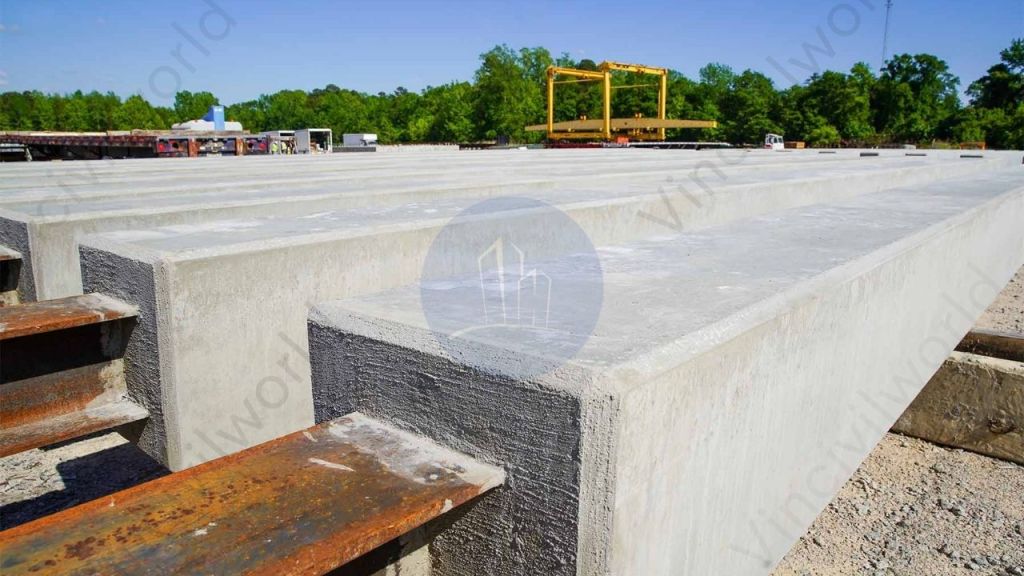
Concrete sheet pile
Concrete sheet piles are retaining walls constructed from precast reinforced concrete sections. We frequently employ them in civil engineering and building projects with a requirement for long-term retaining structures.
We must handle and drive the piles carefully, and provide the necessary reinforcement. The most common application of Concrete sheet pile occurs in deep excavations. These situations arise where soil conditions are unfavourable. In these cases, we require lateral support. They are impermeable and can withstand hydrostatic pressure, making them excellent for usage in places with high water tables. We provide a capping to the heads of the piles by casting a capping beam, while we cut the toes with an oblique face to make driving and interlocking easier. They are relatively heavy and thick, and while driving, they displace significant amounts of the earth.
The driving resistance rises as a result of the considerable volume displacement. Concrete sheet piles are also resistant to weathering, corrosion, and erosion, making them a durable solution under extreme conditions. Concrete sheet piles are available in a range of dimensions and we can interlock them to create a continuous wall. We can place them in a variety of ways, including driving, vibrating, and pushing. The method of installation depends on the accessibility to the site, the depth of the installation, the state of the soil etc.
Concrete sheet piles are a strong and long-lasting alternative. However, their installation may be more costly and time-consuming than that of other retaining wall materials. However, installing them requires large machinery, which can be difficult in places with restricted access or space. Overall, concrete sheet piles are a viable option for permanent retaining walls in deep excavations and severe soil conditions. They are a preferred option due to their strength. They also have resistance to water and erosion, making them ideal for projects involving coastal protection and flood control.
Aluminium sheet piles
Aluminium sheet piles are lightweight, strong, and corrosion-resistant. They are an ideal choice for projects that require a lightweight and durable material.
Composite sheet piles
We manufacture Composite sheet piles from a combination of materials. These include steel and concrete. This combination provides additional strength and durability. They often find applications in projects that require high load-bearing capacity.
Cellular sheet pile
We usually design Cellular sheet pile with hollow sections that allow for increased strength and load-bearing capacity. They find application in projects that requires a high degree of lateral support.
Cold-formed sheet piles
Cold-formed sheet piles are made by bending steel sheets into a desired shape. They find application in projects requiring lower strength and load-bearing capacity.
Conclusion
Each type of sheet pile has its own advantages and disadvantages. The choice of material and design will depend on the specific requirements of the project. Proper design and installation are essential to ensure the stability and safety of the sheet pile wall. You should consult with an experienced engineer before selecting a specific type of sheet pile for a project