Components of a road or parts of a road plays an important part in ensuring the safety and service life of a road. Components of a road is designed to meet the design requirements, functional requirements etc. This article is about the components of road/parts of a road and its functions.
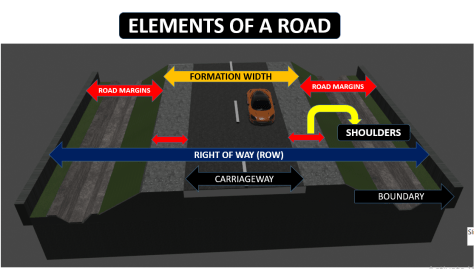
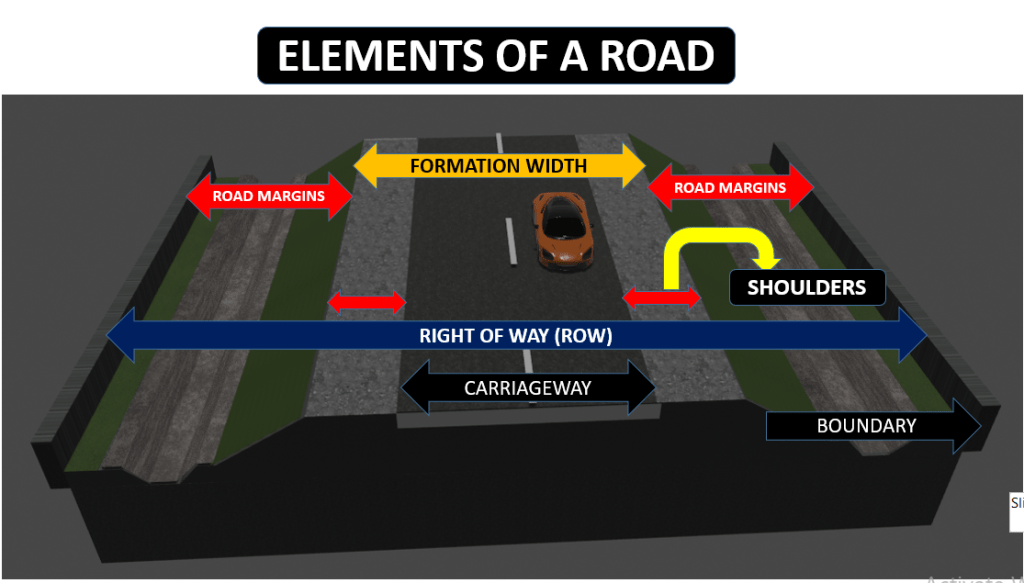
Understanding the road pavement structure is crucial for designing and maintaining effective roadways. Key road components include the carriageway or pavement, roadway or formation width, camber or cross slope, kerbs, medians, road margins, and the right of way (ROW). Each part serves a specific role within the overall road section. This blog will explore these components of the road. It will detail the role of each road section. The blog will explain how they contribute to the road’s durability and performance.
Components of a Road
The road components are crucial for ensuring road durability and safety. Each part of the road, from the carriageway to the right of way (ROW), plays a specific role in the road section. Understanding these components and their functions helps in maintaining effective road performance. The main road sections are listed below.
- Carriage way or pavement
- Road way or formation width
- Camber or cross slope
- Kerbs
- Medians
- Road margins
- Right of way ( ROW)
Video showing the components of a road
Also read : Alignment of road – Factors affecting – obligatory points
Also read : Classification of road – Full details
Carriage way or pavement width
The paved part or surface of the road for traffic movement without any restriction is called the carriageway. The width of the carriageway/ pavement width depends on the number of traffic lanes. The number of lines is decided based on the type of road, service importance, and traffic density.
The carriageway or pavement width is a critical road component that determines the space available for vehicle movement. It directly affects traffic flow, safety, and overall road performance. Properly designed pavement width ensures efficient use of road space and supports the road’s intended load-bearing capacity.
The carriageway is divided into a single carriageway and a dual carriageway as shown in the figure.
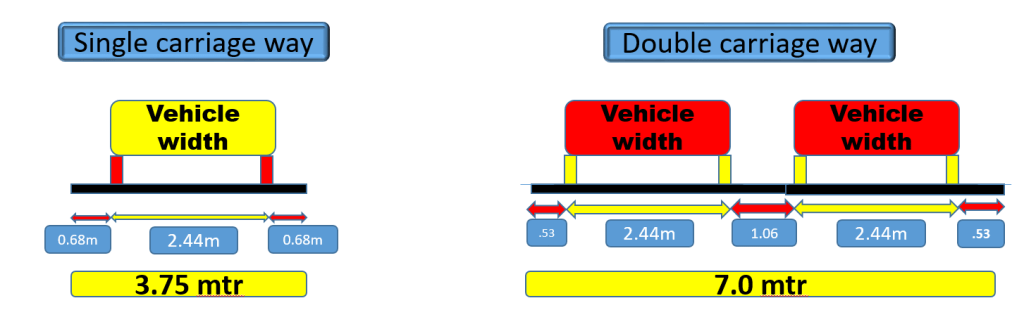
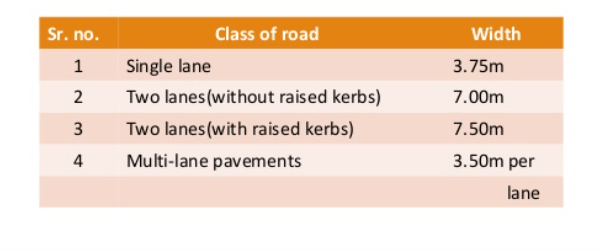
The maximum permissible width of a vehicle is 2.44 and the side clearance for single lane traffic is 0.68 m. The required minimum lane width is 3.75 m for a single lane road. For the dual carriageway, the pavement width is two times 3.75 mtr. ie: 7.5 mtr.
Each country has its own specification for carriage way widths.
Must read : Road pavement layers – Components and function
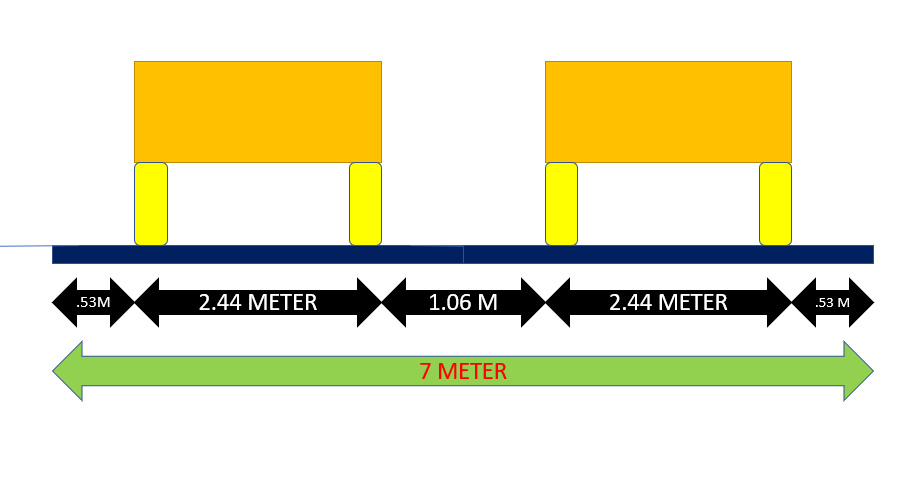
Carriage width as per IRC
Road way or formation width
Width of formation or roadway width is the sum of the widths of pavements or carriage way including separators and shoulders. This does not include the extra land in formation/cutting. (Ref : Diagram)
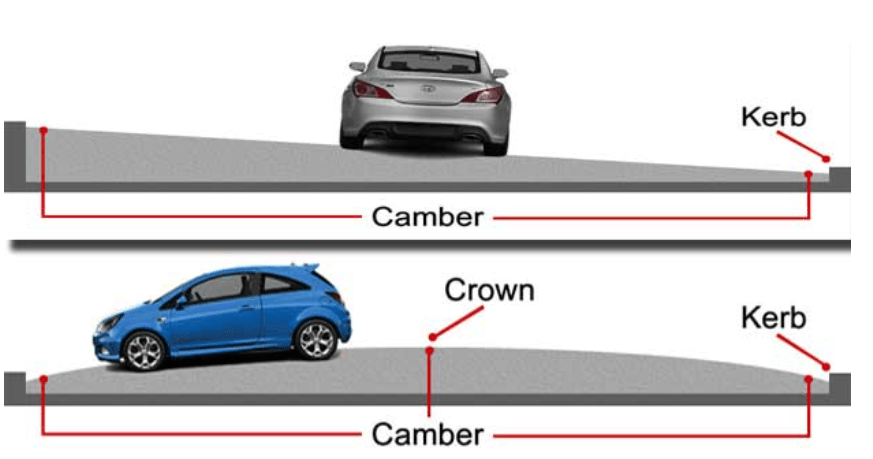
Camber or cross slope
Camber or cross slope provided to raise the middle of the road in the transverse direction to drain of water. Inadequate slopes result in flooding of water on the pavement which may deteriorate the surface in course of time. The too steep slope is undesirable for it will erode the surface.
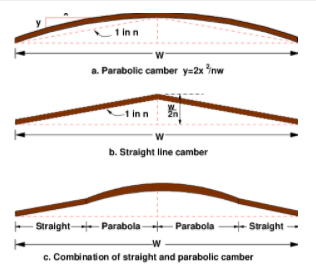
Camber or cross slope serves as Surface protection especially for gravel and bituminous roads. They protect the sub grade by providing proper drainage. This also enables quick drying of pavement. This in turn protects the vehicles from slipping and thereby increases safety.
The value of camber depends on the type of material used for making it and rainfall density in that region.
Kerbs
Kerbs are dividing line between carriage way and shoulders, footpath or islands. The following are the different types of kerbs.
Low or mountable kerbs allows the vehicle to enter the shoulder area with little difficultly. Height of 10 cm above pavement level & Edge will have a slope allowing vehicle to step over easily.
Semi barrier type kerbs are used when the pedestrian traffic is high. Their height is 15 cm above the pavement edge. This type of kerb prevents encroachment of parking vehicles. In an acute emergency, it is possible to drive over this kerb with some difficulty.
Barrier type kerbs are designed to discourage vehicles from leaving the pavement.
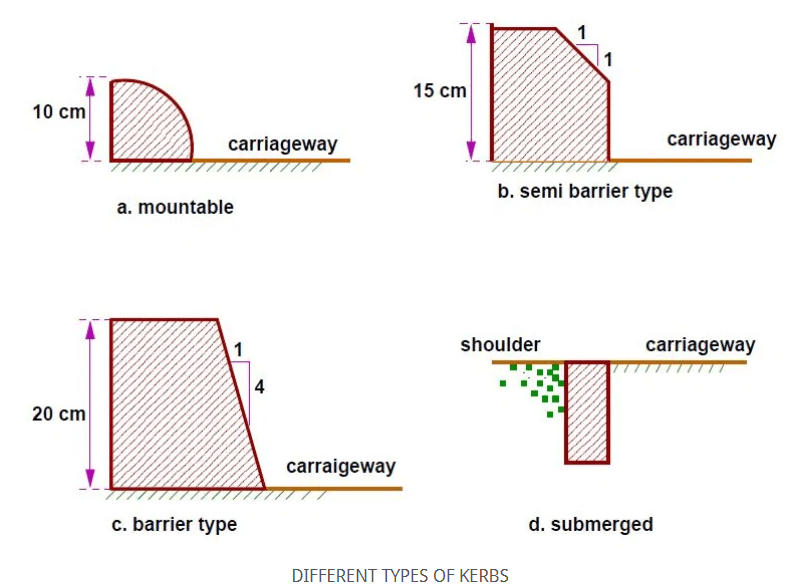
Submerged kerbs are used in rural roads as edges between the pavement edge and shoulders.
Function of kerb
- Drainage control
- Demarking of walkways
- Roadway demarking
- Maintenance assistant
- Assisting road side development.
Medians or traffic separators
They are physical or painted separation provided to separate two road ways. Mainly used to differentiate vehicles based on speed.
Right of way
Right of way or ROW is the land to be acquired for the road along its alignment. The right of way depends on the importance of the road, traffic an possibility of expansion in the future. They include the total elements of the road like carriageway, shoulders, drainage system, cuttings, and embankment slopes, etc.
Factors influencing the width of ROW
a) Width of formation
b) Embankment depth and cutting depth
c) Side slopes of embankment or cutting
d) Drainage system
e) site distance considerations
f) Future widening & Service roads.
Road margins
The portion of the road beyond the carriageway and on the roadway can be generally called road margin. Various elements that form the road margins are given below.
They include
- shoulders
- Parking lines
- Bus bay
- Service roads
- Cycle track
- Footpath
- Guard rail
For more details about road margin : Must Read