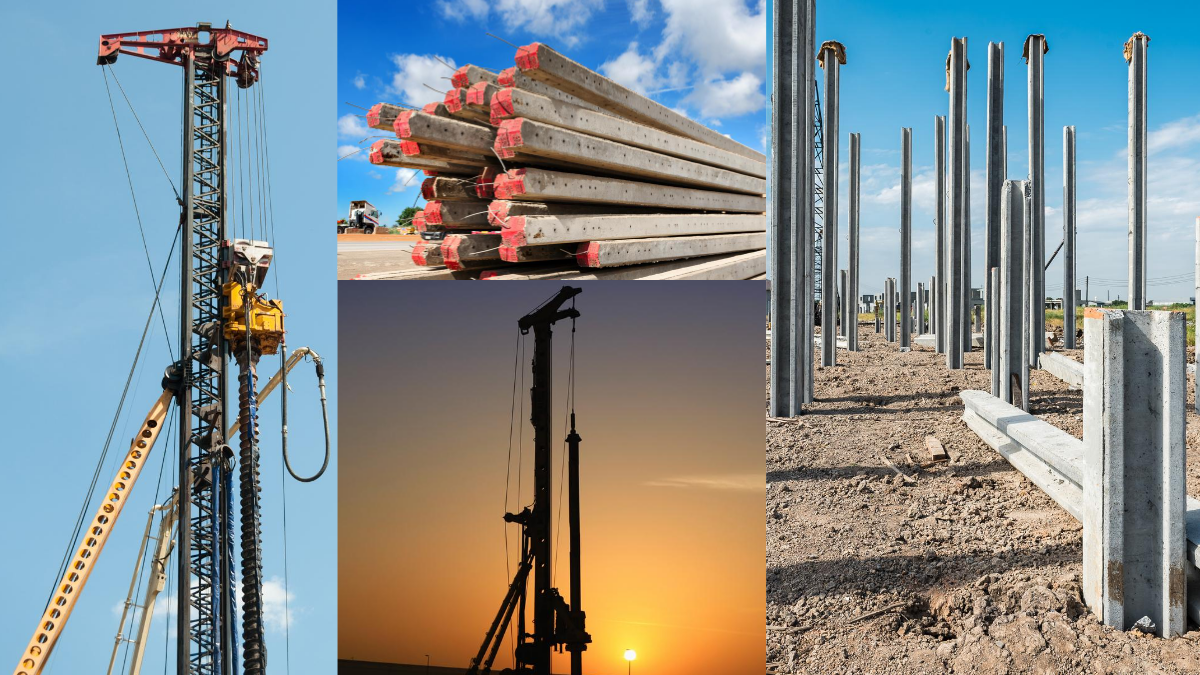
Anchored retaining walls, also known as tie-back systems, are essential structural components used in construction. They are mostly used to stabilize earth and as support structures. Anchored Retaining walls deliver lateral support to walls. They prevent soil from shifting or eroding. These walls are commonly used in applications like deep excavations, embankments, and hillside retention etc.
This article will cover the different types of anchored retaining walls/ tie back systems. This article will also discuss the design principles and the installation process and explore the advantages and applications of using tie-backs in modern construction projects. An anchored retaining wall system is a structural element. This is installed through the rock or soil and transfers the tensile forces developed in the structure to the ground. Anchored retaining walls are often slimmer than all their counterparts like gravity walls and cantilever retaining walls.
- What is an Anchored Retaining Wall?
- Key Components of Tie-Back Retaining Walls
- Design Principles of Anchored Retaining Walls
- Types of Tie back systems
- Anchored retaining wall or Tie back system – Installation method.
- Fixing of anchors in a tie-back system
- Advantages of anchored retaining walls
- Key Takeaways from Anchored Retaining Walls/Tie-Back Systems
- Conclusion
What is an Anchored Retaining Wall?
An anchored retaining wall uses additional reinforcements for stability. Often, these reinforcements are steel cables or rods. They are known as anchors or tie-backs. The tie-backs are driven deep into the ground behind the wall. They anchor the wall securely. This allows it to resist pressure from the retained soil. These walls are ideal for supporting large vertical loads. They are particularly effective when space constraints limit the use of other retention methods.
Key Components of Tie-Back Retaining Walls
Tie-back systems rely on two main components: anchors and retaining walls.
Retaining Wall
The wall itself is usually made of materials like concrete, steel, or timber. It serves as the primary barrier to resist the pressure exerted by the retained soil.
Anchors
These are steel rods or cables inserted into the soil behind the wall, providing tension to counteract the lateral forces exerted by the earth. The anchors are fixed at the back end using a variety of methods, including grouting or mechanical anchoring.
Design Principles of Anchored Retaining Walls
The design of an anchored retaining wall involves several key considerations to ensure structural integrity and durability:
Safety Factors
A safety factor is applied in the design to account for unforeseen stresses or variations in soil conditions.
Soil Type
Understanding the soil characteristics is crucial for determining the number, length, and type of anchors needed.
Load Calculations
Engineers must calculate the lateral earth pressure and any additional loads (such as water pressure) to determine the anchor capacity.
Anchor Spacing
Proper spacing of tie-backs is essential for uniform load distribution and wall stability. The design will vary based on wall height and soil type.
Types of Tie back systems
There are several types of anchored retaining walls, each suited for different applications
Gravity Retaining Walls with Anchors
Gravity retaining walls rely primarily on their own weight to resist the lateral pressures exerted by the retained soil. These walls are usually constructed from concrete, masonry, or stone. They are often designed with added anchors for additional stability. This is especially important in situations with significant soil pressure.
The anchors provide a secure connection to the soil behind the wall. This connection enhances the wall’s ability to withstand overturning and sliding forces. Gravity walls are typically employed for low-height structures where space allows for their robust base design. They are simple to construct and cost-effective for lower applications.
Cantilevered Retaining Walls with Anchors
Cantilevered retaining walls have a unique design. They include a vertical wall supported by a slab. The system also includes a footing. This design efficiently utilizes the wall’s weight and structural integrity. It allows the wall to resist lateral forces. Anchors, which are embedded into the ground behind the wall, aid in this resistance. The additional support provided by the anchors is crucial for taller walls where lateral earth pressures are more significant.
Cantilevered walls are often preferred where space is constrained. They can be designed to accommodate various soil types. This makes them versatile for different applications.
Sheet Pile Walls with Tie-backs
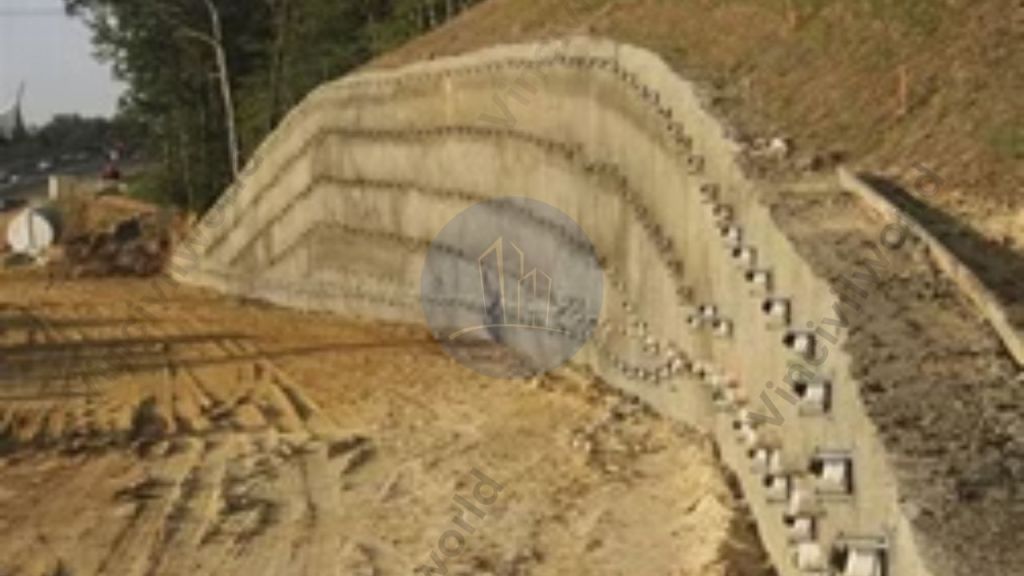
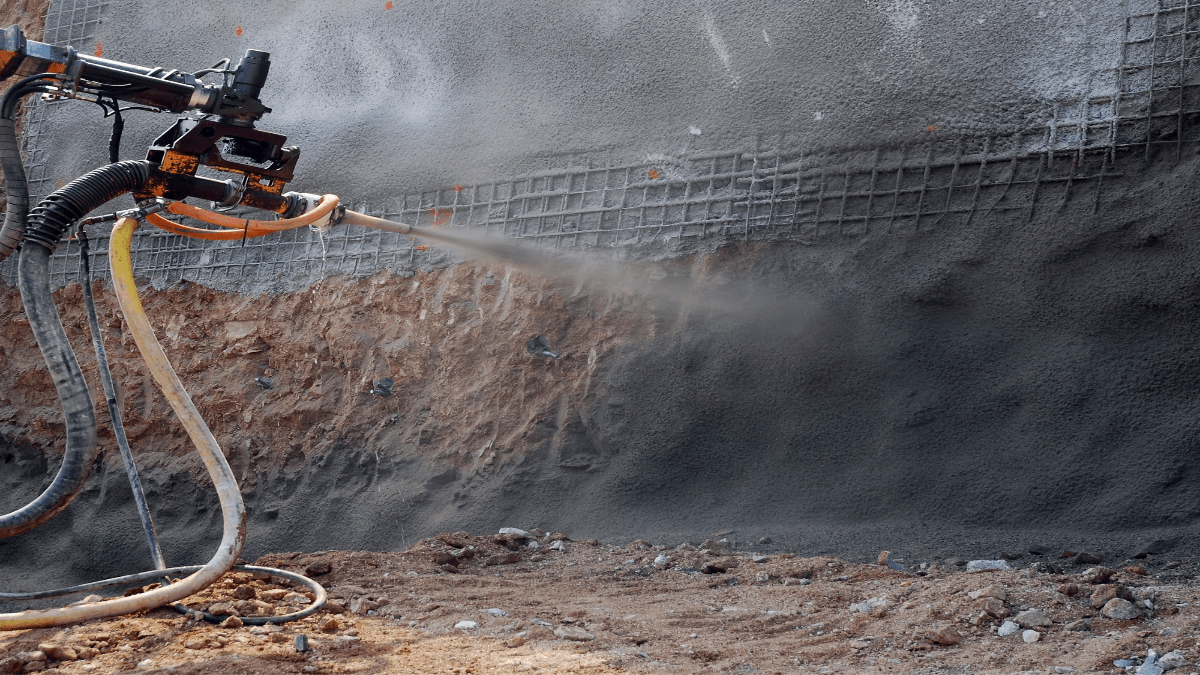
Sheet pile walls are constructed from interlocking steel or concrete sheets. These sheets are driven into the ground to create a barrier against soil and water. This type of wall is particularly effective in deep excavations. It is also suitable for waterfront construction projects. Limited space makes conventional retaining methods impractical in these scenarios. Tie-backs are incorporated to enhance the stability of sheet pile walls. They provide tension forces that counteract lateral earth pressures.
These tie-backs are anchored into the soil or bedrock behind the wall. This system is highly effective in urban settings. It also works well in areas with high groundwater levels. Sheet pile walls with tie-backs offer a reliable solution for managing soil movement and maintaining structural integrity in challenging environments.
Soil Nail Walls
This wall type incorporates soil nails, which are long steel bars inserted into the soil, providing stability through tension. Soil nail walls are ideal for steep slopes and challenging sites. They are cost-effective for moderate heights. They are also less intrusive than other wall types. They allow for better drainage and less disruption to the surrounding area
Braced Walls
Often used in deep excavations, these walls are supported by braces or struts connected to the ground. Braced walls can handle high loads and are versatile for various soil conditions. They require careful planning for spacing and materials to ensure structural integrity while managing excavation risks(
Anchored retaining wall or Tie back system – Installation method.
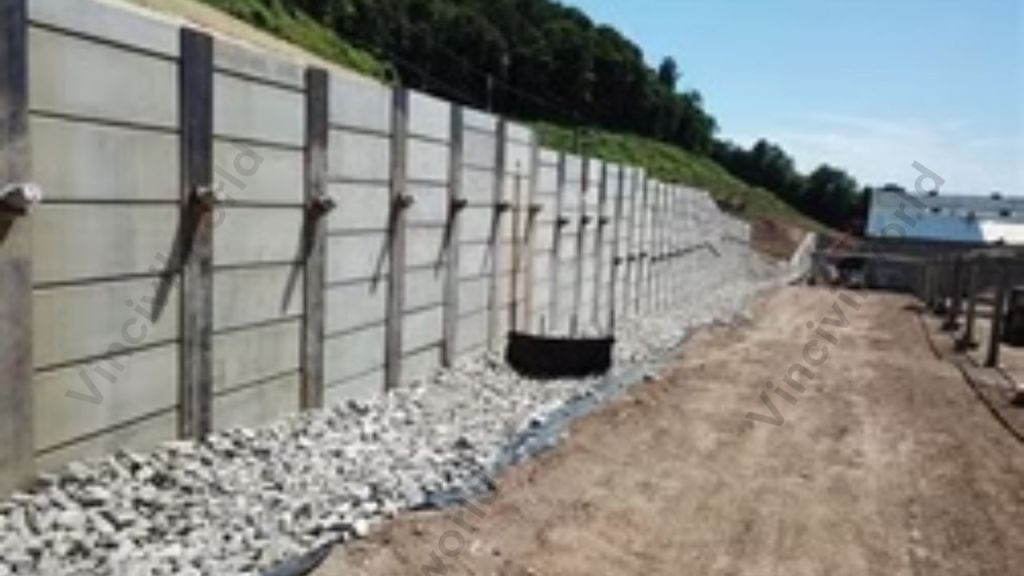
Anchored retaining wall is also known as a tie-back system. They are used in combination with cantilever retaining walls, piled retaining walls, sheet piles, tangent walls, etc. The Tie-back system enhances the stability of the structure. It plays an important role in equipping the walls to handle additional loads.
The anchored walls are installed when the load acting on the structure is high. In this case, the design of cantilever retaining walls / piled retaining walls/ sheet piles etc seems uneconomical. Moreover, it is difficult to accommodate the foundation and structures due to space constraints. For enhancing the load-carrying capacity and economising the structure additional anchors are embedded in the earth to be stabilized. These anchors in combination with the main structure negotiate the loads.
Related posts from vincivilworld
Also Read : Soil Nailing – Installation, Advantages and applications.
Fixing of anchors in a tie-back system
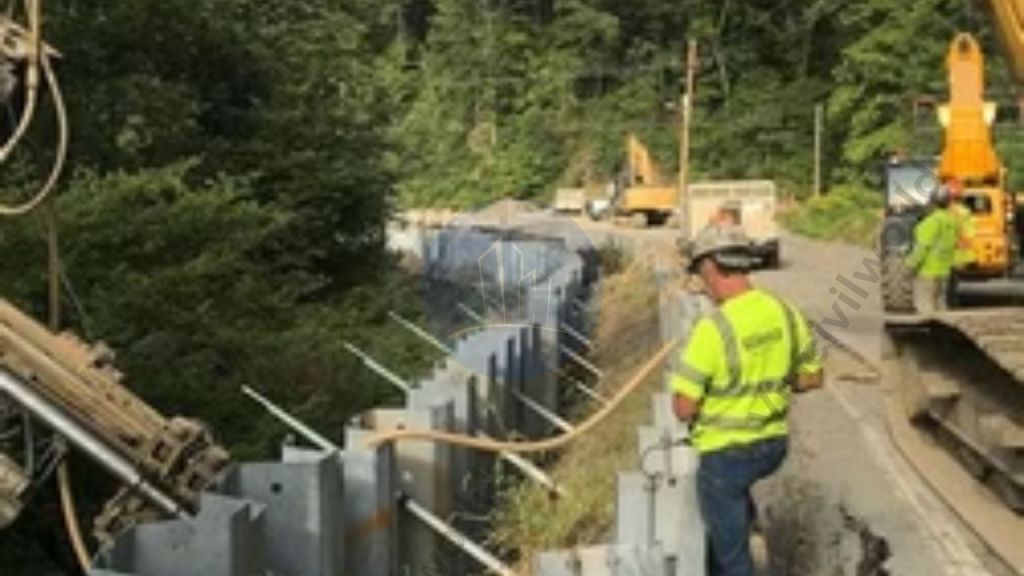
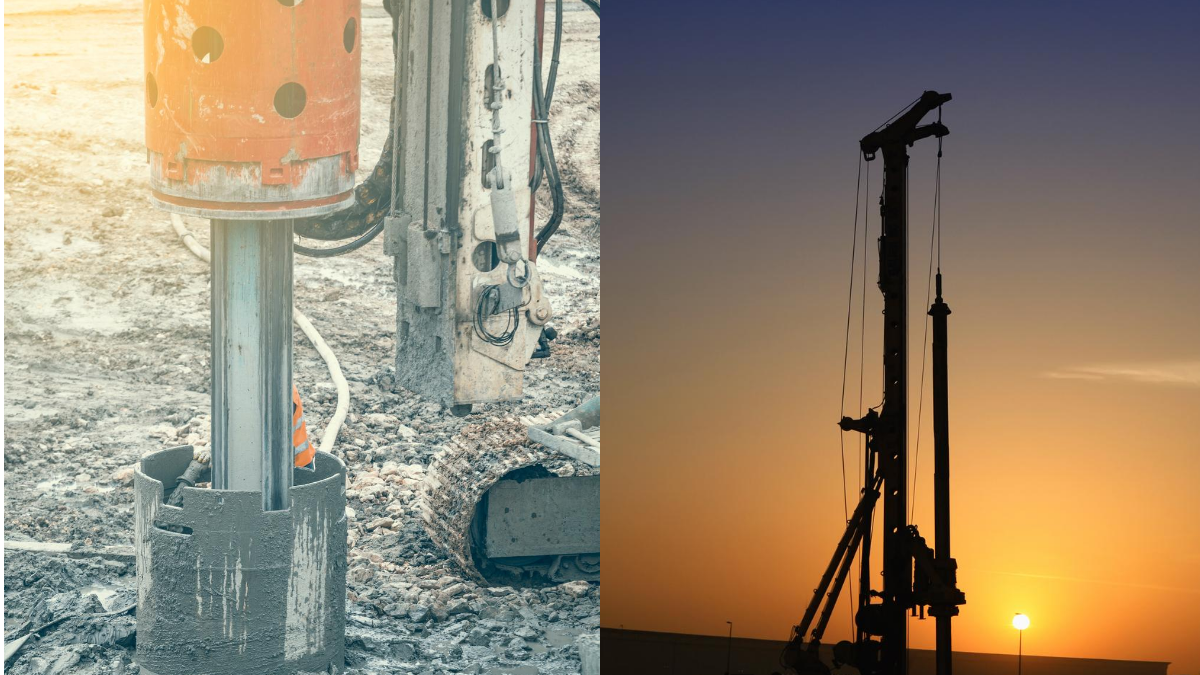
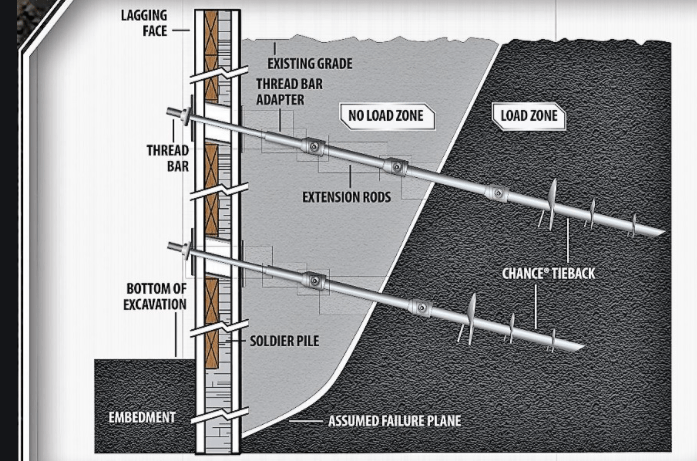
One end of the tieback is anchored to the wall and another end is driven to the soil/rock. Sometimes stable concrete structures are driven into the ground to get a good anchorage. Tiebacks and drilled through the wall to the soil at an angle of around 15-45 degrees.
After drilling the holes ties or struts are provided inside the drilled holes and pressure grouted to give greater stability. In the case of piled retaining walls, the tie-back system is drilled through whaler beams installed between the piles as shown in the figure. Steel rods are placed inside the drilled holes and grouted under high pressure. This creates a bulb-like anchor at the rods’ end, preventing the tie-backs from pulling out the load.
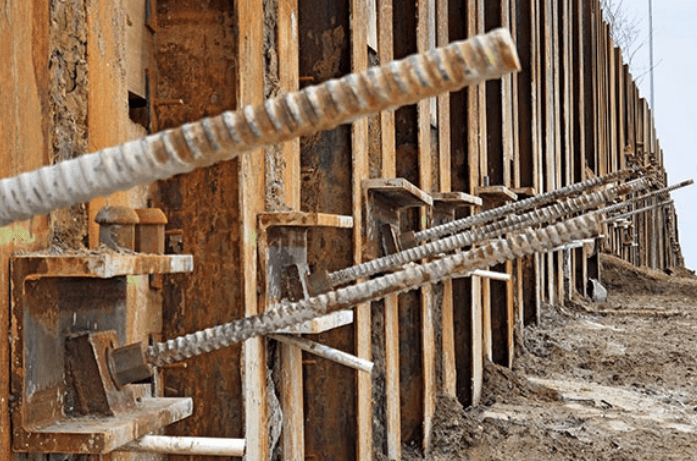



These walls can be very tall and support high loads and are ideal for smaller areas that need earth retention.
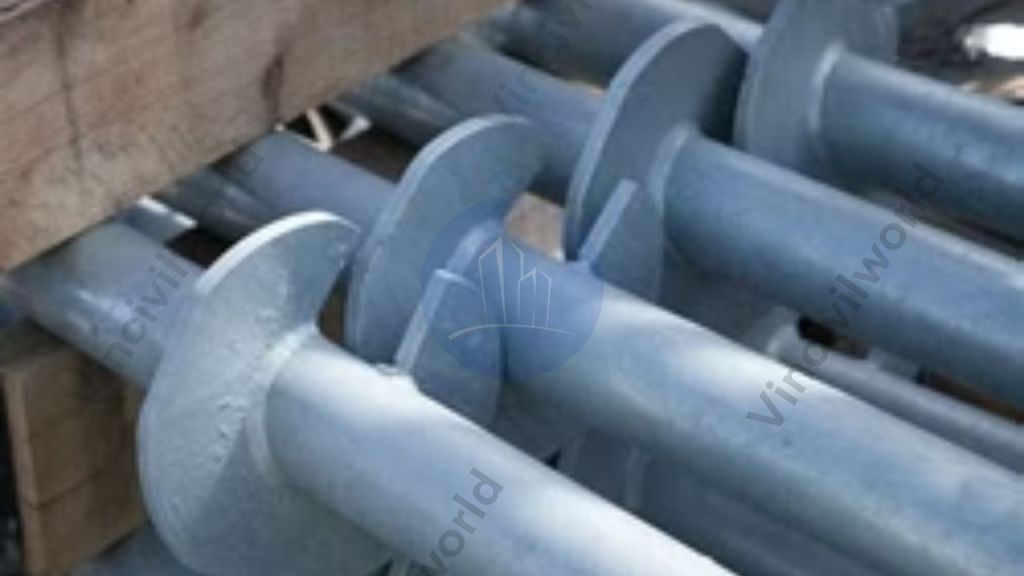
Some times instead of rods, helical anchors are also driven to in place and the capacities are decided by the torque required for tightening the anchors.
The main purpose of the tieback system is to develop a strong soil mass to resist external failure modes. The moment of soil and wall has to be restricted to get better serviceability.
Advantages of anchored retaining walls
- Mostly used for slope protection and retaining earthworks of deep excavations.
- Thin walls or very light structures can be designed in combination with anchored walls.
- Anchored walls are one of the most economical systems of earth retention.
- Combination with sheet piles, cantilever retaining walls, piled retaining walls etc are very useful for deep excavations. They help in providing a safe working area.
Key Takeaways from Anchored Retaining Walls/Tie-Back Systems
- Slope Protection: They are primarily used for stabilizing slopes and retaining earth during deep excavations.
- Thin Wall Design: Anchored retaining walls allow for thinner and lighter wall designs without compromising strength.
- Cost Efficiency: These systems are highly economical for retaining earth compared to other methods.
- Versatility: They can be used with sheet piles, cantilever, and piled retaining walls for various deep excavation projects.
- Space Saving: Suitable for areas with space constraints while maintaining structural integrity.
- Structural Stability: Anchored walls provide lateral support and resist significant external loads, ensuring safety during excavation projects.
Conclusion
Anchored retaining walls, or tie-back systems, play a crucial role in modern construction. Their design provides lateral stability while allowing for thinner and more cost-effective structures. They are particularly useful for deep excavations, slope retention, and projects where space is limited. The combination of anchors with retaining walls makes them adaptable to various applications, from sheet piles to cantilever walls. Anchored retaining walls are among the most economical solutions for ensuring soil stability. They offer versatility, especially in urban or constrained environments. Their integration in construction projects ensures structural safety, cost savings, and effective use of space.
For more details about the retaining walls watch the below video.
Youtube video – 15 Types of Retaining wall systems