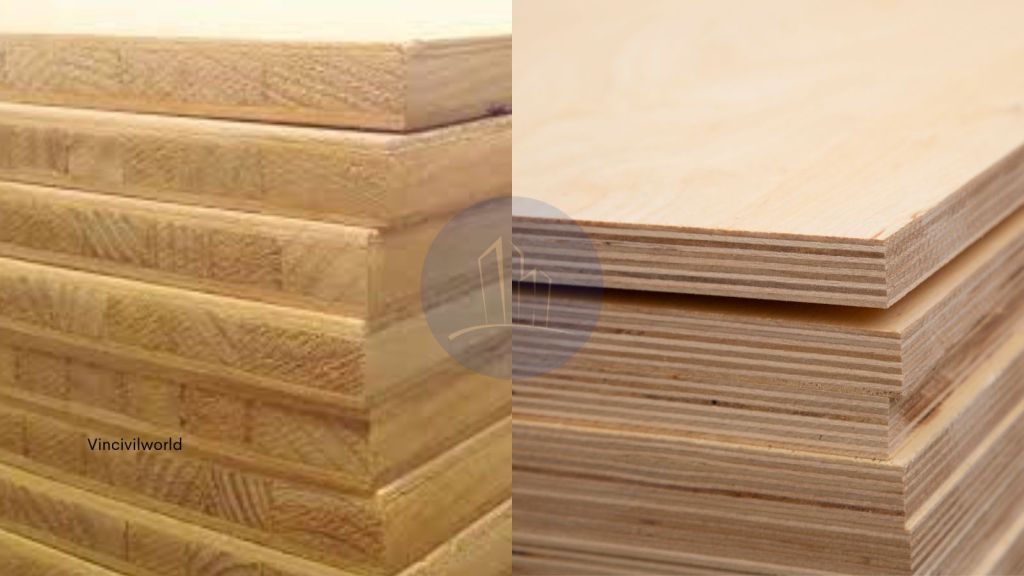
Blockboard vs plywood, Most people get confused with these terms because of the similarity in looks, and both products are popularly used in interior works, home decor, and furniture works. In reality, both these materials are different types of engineered wood and possess entirely different properties, and are used for specific interior applications.
Blockboard, with its core of softwood strips sandwiched between veneers, is known for its strength and durability. In contrast, plywood features multiple layers of thin veneer glued together, providing flexibility and stability. As you weigh plywood vs block board, consider how each material meets your needs for load-bearing, cost, and aesthetics. Blockboard plywood is often preferred for heavy-duty applications, while plywood and blockboard both offer versatility for different uses. This blog explains and clarifies the differences and properties of ply board/block-board and can make the right choice.
- What is plywood?
- What is Plyboard or blockboard?
- Blockboard vs Plywood- A comparison
- Manufacturing process – Blockboard vs Plywood
- Ease of handling – Plywood vs Blockboard
- Strength and durability
- Water and moisture resistant properties
- Physical properties
- Screw holding capacity
- Flexibility in Applications: Blockboard vs Plywood
- Applications: Blockboard vs Plywood
- Sizes available
- Service Life: Blockboard vs Plywood
- Economy
- Sound insulation properties
- Key Takeaways
- Conclusion
What is plywood?
Plywood is an engineered wood panel manufactured by joining sliced wood veneers 2-4 mm thick in a cross-layered pattern and pressed under high temperature to form sheets.Unlike blockboard, plywood is flexible and resistant to warping. This makes it ideal for a wide range of applications, from furniture to construction. When comparing blockboard vs plywood, plywood’s adaptability and ease of use stand out.
Must Read : Plywood Types – MR Resistant ,BWR & BWP or Marine ply
Must Read : WPC board vs plywood – Which is best?
What is Plyboard or blockboard?
Plyboard or blockboard is an engineered wood panel made of a core comprising of softwood wooden strips or blocks placed edge to edges sandwiched between two wood veneer layers. This construction gives it strength and durability, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications like furniture and doors. These veneer layers are glued and pressed under high pressure and temperature to form a plyboard/blockboard. Compared to plywood, blockboard is thicker and provides better load-bearing capacity. When considering blockboard vs plywood, blockboard excels in situations requiring robust support and rigidity.
Also read : WPC Boards – Advantages, Disadvantages and uses
Blockboard vs Plywood- A comparison
Let us have a comparison between the properties , types and uses of Plyboard and plywood/blockboard. This comparison highlights key differences to help you choose the best material for your project.
- Composition and Manufacturing process
- Ease of handling
- Strength and durability
- Water and moisture resistant properties
- Physical properties
- Screw Holding capacity
- Flexibility in applications
- Sound insulation properties
- Sizes available
- Economy
- Service life
Manufacturing process – Blockboard vs Plywood
| Blockboard/Plyboard | Plywood |
| Small wooden strips are placed edge to edge sandwiched between sliced wooden veneers. | Plywood is made in an odd number of veneer layers starting from 3 layers more depending on the thickness of the plywood. |
| Block boards are made in either 3 layers or 5 layers. It is like a wooden frame filled with small wooden strips and covered by wooden veneers on the faces. | The veneers are arranged in a cross layered pattern. |
Blockboard vs plywood involves different core materials and manufacturing methods. Blockboard has a core of softwood strips with outer veneers, while plywood features alternating layers of veneer. Each method affects the material’s strength, flexibility, and final use.
Ease of handling – Plywood vs Blockboard
| Blockboard/plyboard | Plywood |
| Blockboard mostly uses softwood core and hence blockboard is lighter than plywood. | Plywood grades use dense hardwood and the layers are pressed to form plywood. |
| Due to their lightweight nature, they are easy to transport and handle. | plywood is solid and heavier than Blockboard. |
Blockboard uses softwood for its core, making it lighter compared to plywood, which uses dense hardwood veneers. Consequently, blockboard is easier to handle and move, while plywood’s weight can make it more challenging to work with.
Strength and durability
| Plyboard/Blockboard | Plywood |
| Mostly uses softwood in the core. Softwoods are soft and have low strength and hence blockboards have moderate strength. | Mostly uses hardwood veneers arranged in a uniform cross-layered pattern. Plywood is much stronger than blockboard. |
| Plyboard is strong compared to particleboard and MDF but is less durable as compared to plywood. | Low-density plywood can even take moderate loads. They are strong and durable when compared with blockboards/plyboards. |
| Blockboard looks plain from the outside, but minor gaps are inside the core. | Plywood layers are uniform in both directions and no gaps will be there. |
Blockboard provides robust strength due to its core of softwood strips, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications. However, it can be affected by moisture. Plywood, with its layered veneer construction, offers consistent strength and high durability, making it resistant to environmental changes and suitable for diverse uses.
Water and moisture resistant properties
| Plyboard/Blockboard | Plywood |
| Blockboards retains moisture and more prone to water and moisture damages. | Plywood grades like BWR (Exterior Grade)and Marine ply are less suspectable to water and moisture. |
| They can be made waterproof by using BWP Grade (Boiling Water Proof) resin for bonding the strips. | Plywood grades like BWR (303 grade) and Marine ply (710 grade) are superior to block boards in terms of moisture and water-resistant properties. |
Physical properties
| Plyboard/Blockboard | Plywood |
| Bending and sagging | |
| Plyboard is more stiffer than plywood and do not bend when used as long pieces. Block board is preferred over plywood when used as lengthy panels and furniture. | Long pieces of plywood may sags from the centre. Plywood is less stiffer than blockboard. |
| Warping and Cracking | |
| It has good dimensional stability and so is highly resistant to warping and cracking | It is resistant to warping and cracking. |
| Splitting on edges | |
| Plyboard does not split on edges while cutting | Plywood split on edges while cutting. |
| Block board is comparatively easy to cut. | Plywood splinter on edges and is very difficult to cut. |
Blockboard vs plywood differs in density, thickness, and other physical properties. Blockboard, with its softwood core, is typically thicker and less flexible but provides a smooth surface. Plywood, made from layered veneers, is denser, more flexible, and offers better dimensional stability.
Screw holding capacity
| Plyboard/Blockboard | Plywood |
| Blockboards have very good screw holding capacity, than particle board and MDF. They can hold nails very well and thus are used for making custom made furniture. Also they are used as core in flush doors, where screw holding capacity is essential. | Got excellent screw holding capacity due to the cross layered arrangement of veneers. The hinges do not come out easily. |
| Some times the screws tend to go between the gaps of the wood pieces. Skilled carpenters can identify and manage the problem |
In the blockboard vs plywood comparison, plywood typically offers better screw holding capacity. The layered veneer structure of plywood provides more grip, making it suitable for applications where secure fastening is essential. Blockboard, with its softer core, may have screws loosen over time and is less reliable for high-stress fastening.
Flexibility in Applications: Blockboard vs Plywood
| Aspect | Blockboard | Plywood |
|---|---|---|
| Application Versatility | Less versatile; best suited for applications requiring solid and stable support, such as heavy-duty furniture and doors. | Highly versatile; used in a wide range of applications including cabinetry, wall panels, and structural components. |
| Customizability | Limited in terms of bending or shaping; typically used in flat applications. | More flexible; can be easily cut, bent, and shaped for various designs and structures. |
| Use Cases | Ideal for applications requiring strength and stability but less flexibility. | Ideal for both structural and decorative purposes due to its adaptability and ease of modification. |
Plywood is more flexible in applications due to its ability to be shaped and customized easily. In contrast, blockboard is less adaptable, making it suitable primarily for stable, heavy-duty applications.
Applications: Blockboard vs Plywood
| Aspect | Blockboard | Plywood |
|---|---|---|
| Typical Uses | Commonly used for heavy-duty furniture, long bookshelves, benches, doors, partitions, and panels where solid support is needed. | Widely used in cabinetry, wall paneling, flooring, structural components, and various DIY projects due to its versatility. |
| Suitability for Interior Design | Suitable for high-end furniture and cabinetry where a smooth finish and robustness are required. | Ideal for a broad range of interior design projects, including furniture, shelving, and decorative panels. |
| Structural Uses | Best for applications requiring solid core strength but less flexibility in design. | Common in structural applications like roof sheathing, subflooring, and wall sheathing due to its strength and flexibility. |
Blockboard is ideal for applications needing solid support, such as heavy-duty furniture and doors. Plywood, being versatile and flexible, is used in a wide range of applications from cabinetry and wall paneling to structural components.
Sizes available
Plywood
- The most commonly manufactured plywood size is 8 x 4 ft. (2449 x 1219 mm)
- It is available in various thicknesses ranging from 3 mm to 25 mm.
Blockboard
- The most commonly manufactured and sold block board size in India is 8 x 4 ft. (2449 x 1219 mm).
- Available thickness are 16mm,19mm,25mm
Service Life: Blockboard vs Plywood
| Aspect | Blockboard | Plywood |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | Generally durable but may have a shorter service life if exposed to moisture without proper sealing. | Highly durable with a longer service life, resistant to environmental changes and moisture when properly treated.Always use BWR and Marine ply for water prone areas. |
| Maintenance | Requires regular maintenance and sealing to extend service life, particularly in humid conditions. | Low maintenance; retains durability with minimal upkeep and resists moisture and environmental factors effectively. |
| Longevity | Suitable for applications where moderate longevity is acceptable but may degrade faster under adverse conditions. | Ideal for long-term use; maintains performance and appearance over extended periods. |
Plywood generally has a longer service life compared to blockboard. While blockboard is durable, it may require more maintenance and protection from moisture to ensure longevity. Plywood, on the other hand, offers extended durability and requires less maintenance, making it suitable for long-term applications.Blockboard should be kept away from water and moisture. They got a better life and durability compared to MDF and particle boards. Blockboards are available in BWR and BWP varieties. They can resist moisture better.
Economy
Blockboard is comparatively cheaper than plywood.
Sound insulation properties
Block boards are poor conductor of sound, heat and electricity and offer good sound and thermal insulation properties.Hence are used in partitions etc.
Key Takeaways
- Blockboard: Lighter than plywood, ideal for heavy-duty applications requiring solid support and stability.
- Plywood: More versatile and flexible, suitable for a wide range of applications including structural and decorative uses.
- Strength & Durability: Plywood is generally stronger and more durable, especially in moisture-prone areas.
- Screw Holding Capacity: Plywood offers better screw holding due to its dense veneer layers.
- Service Life: Plywood has a longer service life with lower maintenance needs, while blockboard requires more care, especially in humid conditions.
- Economy: Blockboard is usually cheaper, making it a budget-friendly option for certain applications.
Conclusion
When choosing between blockboard and plywood, it is essential to consider the specific requirements of your project. Blockboard is an excellent choice for heavy-duty furniture, doors, and long shelves, offering solid support at a lower cost. However, it requires careful handling in moisture-prone areas to ensure durability. Plywood, with its superior strength, flexibility, and moisture resistance, is the preferred material for a broad range of applications, from structural elements to decorative finishes. Its longer service life and lower maintenance needs make it a reliable choice for both residential and commercial projects. Ultimately, your selection should align with your project’s demands, budget, and expected longevity.
Must Read : Plywood vs Natural wood – which is best?