MSE Retaining Walls are also known as Mechanically Stabilised Earth (MSE) retaining walls. Commonly referred to as RE walls, they are a popular choice in modern construction due to their durability and cost-effectiveness. MSE retaining walls consist of layers of soil. The soil is reinforced with materials like geogrids or steel strips. This reinforcement provides essential stability against earth pressures. In this blog, we will explore the meaning of MSE walls, delve into their key components, and highlight their advantages. Additionally, we will examine real-world applications of MSE retaining walls and discuss important design considerations. By comparing RE walls with other retaining wall systems, you will gain a clear understanding of their features. This will help you decide their suitability for various construction projects.
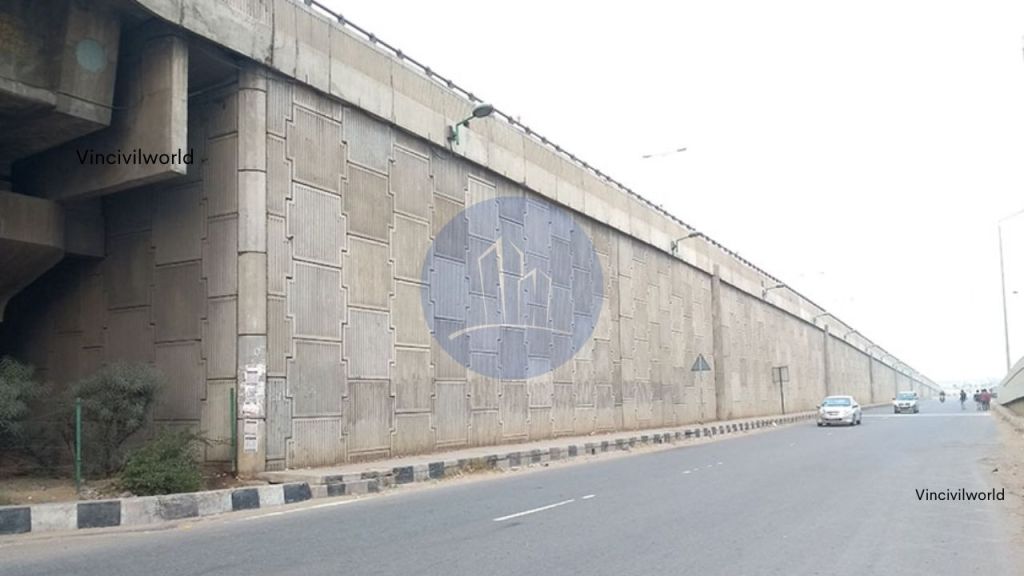
MSE retaining walls means mechanically stabilised earth or reinforced earth. This is an earth retaining system where compacted granular soil is reinforced with horizontal layers of steel strips or geo-synthetic materials. This compacted earth is held together with thin facing elements made of Precast concrete, shotcrete or weld mesh reinforced panels. They are used extensively for constructing retaining walls, bridge abutments, highway wall systems, dykes, etc. MSE retaining walls cost almost half what a concrete structure would have cost for similar uses.
- What is an MSE Retaining Wall?
- Design basis of RE walls/MSE walls
- Components of a MSE retaining wall
- Advantages of MSE walls
- Disadvantages of MSE retaining walls.
- Key Takeaways
- Conclusion
What is an MSE Retaining Wall?
An MSE retaining wall is also known as a Mechanically Stabilised Earth retaining wall. It is a structure designed to retain soil using layers of reinforced materials. MSE walls consist of compacted soil, reinforced with elements like geogrids or steel strips, providing stability against earth pressures. Often referred to as RE walls, these structures are popular due to their durability and cost-efficiency. To grasp the meaning of MSE walls, it’s essential to understand that the reinforcement materials bind the soil. This binding makes the wall robust and stable. MSE retaining walls are widely used in various construction projects, offering a reliable solution for earth retention.
Design basis of RE walls/MSE walls
When designing an MSE retaining wall, consider soil properties, such as bearing capacity and drainage, to ensure stability. Select appropriate reinforcement materials like geogrids or steel strips based on load requirements. Proper wall height and slope must be determined to manage earth pressures. Additionally, incorporate effective drainage systems to prevent water buildup behind the RE wall.
Components of a MSE retaining wall
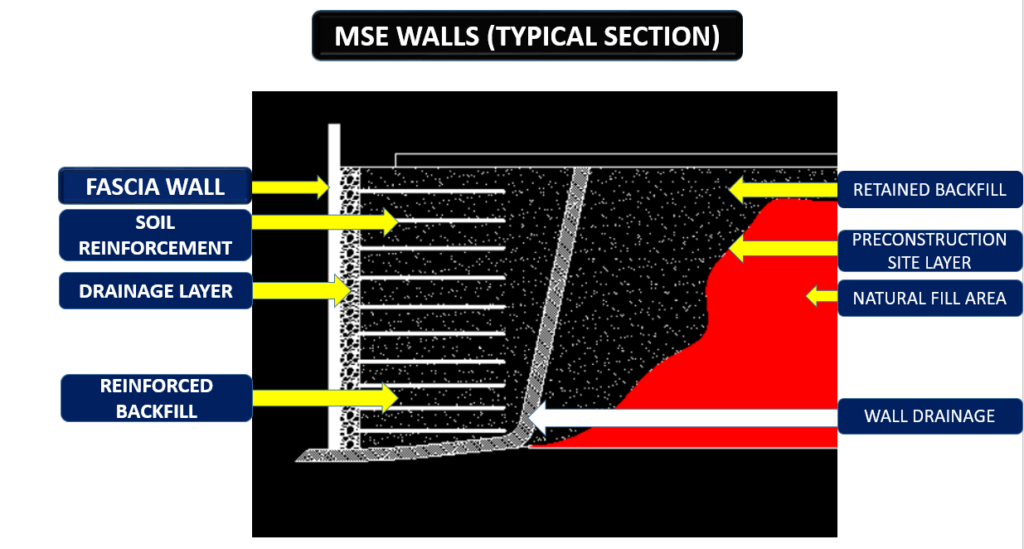
An MSE retaining wall consists of several critical components that work together to provide stability and strength. These RE wall components include reinforced soil layers, facing panels, and drainage systems. The mechanically stabilised earth retaining wall relies on the interaction between the soil and reinforcement materials. Examples of these materials include geogrids or steel strips. This interaction helps to withstand earth pressures. Understanding these key elements is essential for designing a durable and effective MSE wall. The key components of a RE wall system is as follows.
a) Reinforcing element
b) Back fill materials
c) Fascia element
Reinforcement element
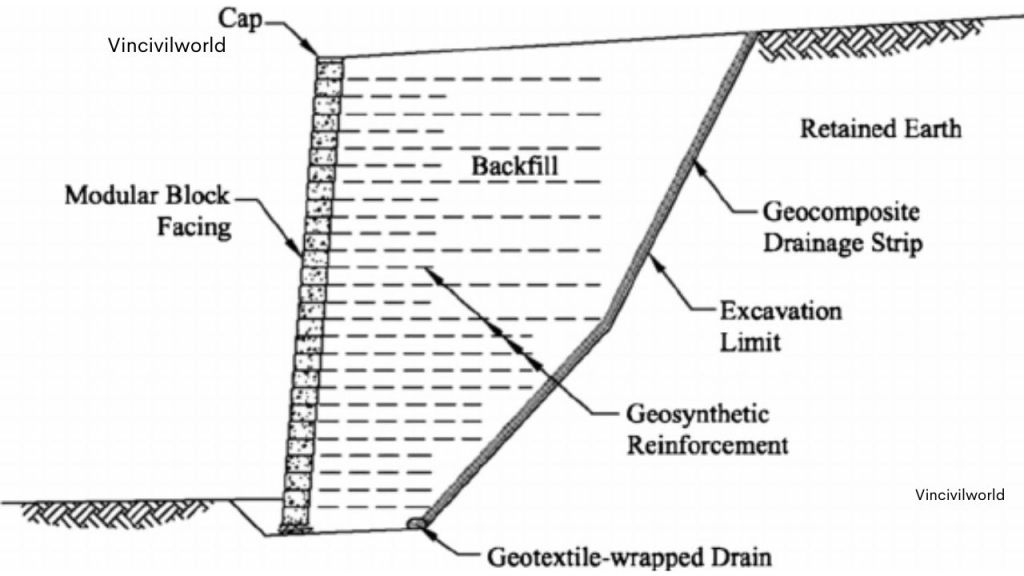
The reinforcing elements of an MSE retaining wall are vital for its stability and strength. These elements typically include geogrids, steel strips, or geotextiles, which are embedded within the soil layers. The reinforcing materials work by binding the soil, creating a unified mass that resists earth pressures. In a mechanically stabilised earth retaining wall, these elements effectively distribute loads and prevent the wall from shifting or collapsing. The careful selection and installation of reinforcing elements are crucial for ensuring the long-term durability and performance of the RE wall.
The reinforcements are used to reinforce and provides the requisite tensile strength to hold the soil together. Two types of reinforcing elements are used in MSE walls. They are metallic and polymeric reinforcements. Metallic reinforcements (In-extensible) include Galvanised iron ribbed strips (50mm-100mm) or ladder strip arrangements.
Polymeric reinforcement (Extensible reinforcement) could be geo-grids or geo-textiles, which are preferred in corrosive environments. For any vertical and horizontal obstructions, reinforcements are bend at an angle, not more than 15 degrees.
Appropriate connections hooks are embedded behind the fascia walls for the anchorage of geo-grids and metal reinforcements.
Back fill materials
For an MSE retaining wall, it is essential that the selected backfill materials are cohesionless. They must meet strict criteria, including gradation, plasticity, organic content, and electrochemical properties. These materials must be free-draining with minimal fine content. The soil friction angle for the MSE retaining wall must be verified by shear tests. The angle of interface friction between the compacted fill and the reinforcing element should be no less than 30 degrees, as specified by IS 13326 Part 1.
Fly ash can be used as backfill for the RE wall, provided it adheres to applicable standards. The selected backfill should be placed parallel to the MSE retaining wall. It should start approximately three feet from the back of the wall panels. The backfill should be compacted in 6-inch lifts. Additionally, soil materials may be placed without reinforcement between the stabilised zone and the natural ground surface. This is known as retained backfill. It ensures the stability and effectiveness of the mechanically stabilised earth retaining wall.
Facing elements
Facing elements in an MSE retaining wall serve to retain filled materials. They prevent local slumping on steeply sloping faces. They also align with both structural and aesthetic requirements. These facings are commonly made of materials such as precast reinforced cement concrete, plain concrete hollow blocks, or similar components.
Drainage layer
For the RE wall, it is essential to incorporate a suitable drainage system in the embankment area. This prevents water logging. A drainage layer, approximately 2-3 feet wide, is installed on the backside of the mechanically stabilised earth retaining wall. This layer uses free-draining material to facilitate proper water drainage from the reinforcement zones. This ensures the stability and effectiveness of the MSE retaining wall.
Jointing and filling materials
Rubber or wooden bearing pads are used between horizontal joints of facing elements. This ensures there shall not be any concrete to concrete joints. The interior panel joints are sealed with geotextile filler cloth in the horizontal and vertical directions as shown in fig. This is done to ensure that no interior back fill materials sweep through the joints.
RUBBER PADS AND GEO TEXTILE LAYER
Advantages of MSE walls
MSE walls, or Mechanically Stabilised Earth walls, are favored for their economic and construction benefits. They enable rapid and efficient construction with minimal disruption to traffic and other services. MSE retaining walls offer a variety of materials and customization options, enhancing their popularity as earth-retaining systems. The fascia elements, backfill, and reinforcing system work together to form a gravity retaining structure. This structure relies on the self-weight of the reinforced soil mass. It resists lateral pressures from earth, service loads, seismic forces, and hydrostatic pressure. The flexibility and efficiency of RE walls make them a top choice in modern construction.
- Heavy Load Capacity: Can support extremely heavy loads such as bridge abutment footings, crane loads, and service loads.
- Seismic and Dynamic Resistance: Designed to resist seismic and dynamic forces, distributing bearing pressure over a wide area.
- Faster Construction: Enables quicker construction compared to conventional retaining walls.
- Minimal Site Preparation: Requires less site preparation and can be built in confined areas where other retaining walls are impractical.
- No Additional Supports: No need for additional supports, finishes, or curing time.
- Free Drainage: Granular backfill facilitates free drainage through panel joints, reducing hydrostatic pressure.
- Lightweight and Precast Fascia: Fascia walls are lightweight, precast, and easily transported and lifted using simple equipment.
- Customizable: Can be made to any height, customized for designs and logos, and adjusted to manage obstructions.
- Versatile Construction: Can be tailored to any geometry, requiring no heavy machinery or specialized workers.
- Durable Service Life: Provides a long service life even under extreme loading and complex conditions.
Disadvantages of MSE retaining walls.
- MSE retaining walls require granular material in huge quantities. Areas where there is a scarcity of granular material the construction cost increase and make the structure uneconomical.
- The corrosion or reinforcement and deterioration of geo-grids on exposed to sunlight has to be addressed. The reinforced component must be designed to withstand erosion and corrosion processes. These processes can highly deteriorate the mechanical behavior of the composite structure.
- Proper drainage system should be provided.
- The wall must obtain a minimum width in order to acquire adequate stability
Key Takeaways
- MSE Walls: Mechanically Stabilised Earth (MSE) retaining walls, also known as RE walls, offer durability and cost-efficiency.
- Components: Include reinforcing elements (geogrids, steel strips), backfill materials, facing elements, drainage layers, and jointing materials.
- Load Capacity: Capable of supporting heavy loads like bridge abutment footings and crane loads.
- Seismic Resistance: Designed to handle seismic and dynamic forces effectively.
- Construction Speed: Allows for rapid and efficient construction with minimal disruption.
- Customization: Flexible design options for various geometries and aesthetics.
- Free Drainage: Ensures effective water management to prevent hydrostatic pressure buildup.
- Durability: Long service life even under extreme conditions.
Conclusion
MSE retaining walls, or Mechanically Stabilised Earth walls, present a robust and economical solution for earth retention in modern construction. Their design incorporates various components, including reinforcing elements, backfill materials, and drainage systems, to ensure stability and functionality. MSE walls excel in supporting heavy loads, resisting seismic forces, and allowing rapid construction with minimal disruption. Customizable and versatile, they offer long-term durability and can be adapted to diverse project requirements. However, challenges such as the need for granular material and addressing potential reinforcement corrosion must be managed. Overall, MSE walls are a valuable option for efficient and effective retaining wall systems.







What an informative article you have here! Surely everyone who’s going to read will learn something from this, big or small, it will help them a lot on deciding the correct wall for their establishment. We at Johnson City Walls & Patios can get you on the right track for that, whether it’s for building a home for you and your family or premises for your own organization!
LikeLiked by 1 person
A retaining wall serves to keep soil in place. This mostly applies to landscapes featuring small hills where these walls act as a necessary barrier to prevent the soil from sliding forward in a landslide.https://easttnoutdoorservices.com
LikeLike