Retaining walls are rigid structures used for supporting soil laterally and retained at different levels on the two sides. These structures are vertical or near-vertical. They are constructed to hold soil between two terrains when the slope exceeds the natural angle of repose. The slope can be vertical or steep or much above the range of angle of repose. Understanding retaining wall types is crucial for selecting the right wall based on soil conditions, load requirements, and project design.
Key retaining wall types include gravity retaining walls. These rely on weight for stability. Buttress retaining walls provide extra support. Elements like retaining wall heel and toe enhance stability, making these walls effective and durable solutions.
This article is about the types of retaining walls, materials used and features.
What is a retaining wall?
Retaining walls are critical engineering structures designed to stabilize and support terrain by restraining soil mass at different elevations. These versatile architectural elements are essential in landscape design, civil engineering, and construction projects. They prevent erosion, manage slope stability, create usable spaces on uneven terrain. Retaining walls provide critical structural support in areas with significant elevation changes.
Engineers and landscape architects utilize various types of retaining walls, each with unique characteristics and applications. The selection depends on factors such as soil conditions and load requirements. Other considerations include site topography, budget constraints, aesthetic considerations, and project design. These factors ensure long-term durability and safety. Common retaining wall types include gravity walls, cantilever walls, and anchored walls, each using distinct methods to provide stability.
Design criteria of retaining wall
The main criteria behind the design of the retaining wall are to counter the downward slope movement of back filled soil by gravity. The lateral pressure developed behind the wall depends on the angle of internal friction & cohesive strength of retained materials. The lateral pressure can also be liquid (hydro-static pressure), and pressure from any type of back-fill material like sand, granular material, fly ash, etc. A proper drainage system is to be provided to reduce the hydro-static pressure.
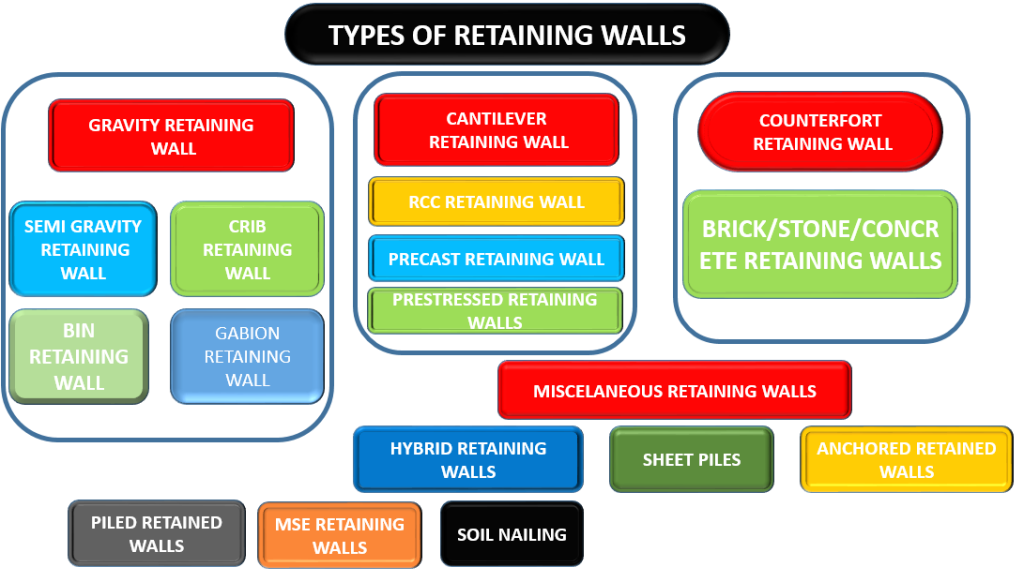
Retaining wall types
There are several types of retaining wall depends on the nature and type of soil and situations they are to be used.
- Gravity retaining wall
- Cantilever retaining walls
- Counter-fort retaining wall
- Buttressed retaining wall
- Sheet pile retaining wall
- Bored pile retaining wall
- Anchored retaining wall
There are a lot of innovative and alternated methods used for retaining walls
Gravity Retaining walls
Gravity retaining walls are executed with stone, bricks, concrete, or any other heavy material. They are done with or without mortar and are designed to counter back-fill soil pressure by their self-weight.
Dry retaining walls do not require rigid footing. However, they must be designed to counter sliding. They also need to address overturning and bearing loads acting on the structure.
These types of retaining walls are mainly adopted in landscape areas and also in locations with height is around 2-3 meters.
Gravity retaining walls are used for larger heights using composite gravity walls. Composite gravity walls include precast crib walls or timber walls filled with granular materials, Gabion walls, Geowalls, etc.
The gravity wall when provided with a small amount of reinforcement is known as semi gravity retaining wall. The load transfer mechanism remains the same as that of gravity retaining walls.
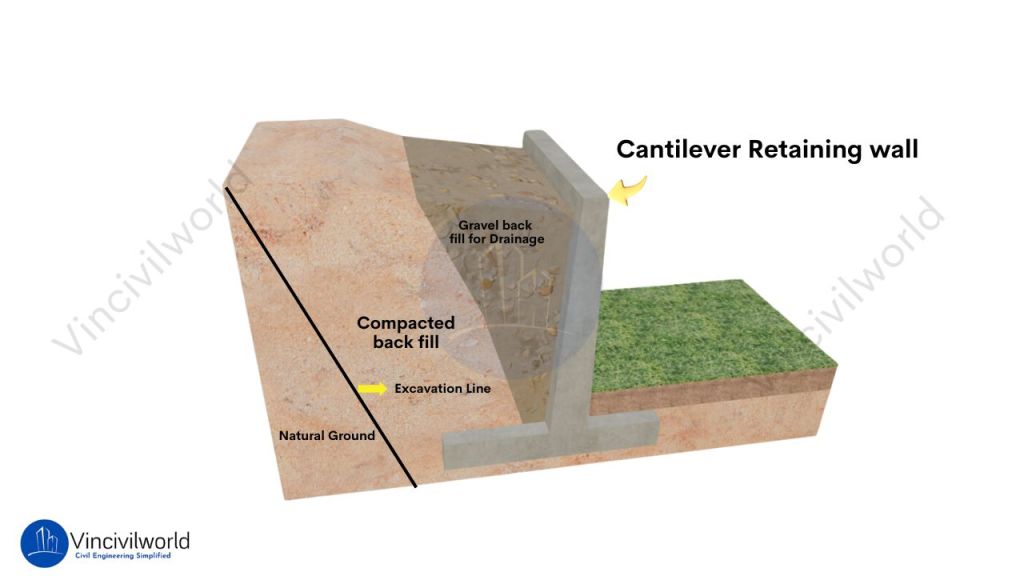
Cantilever retaining walls
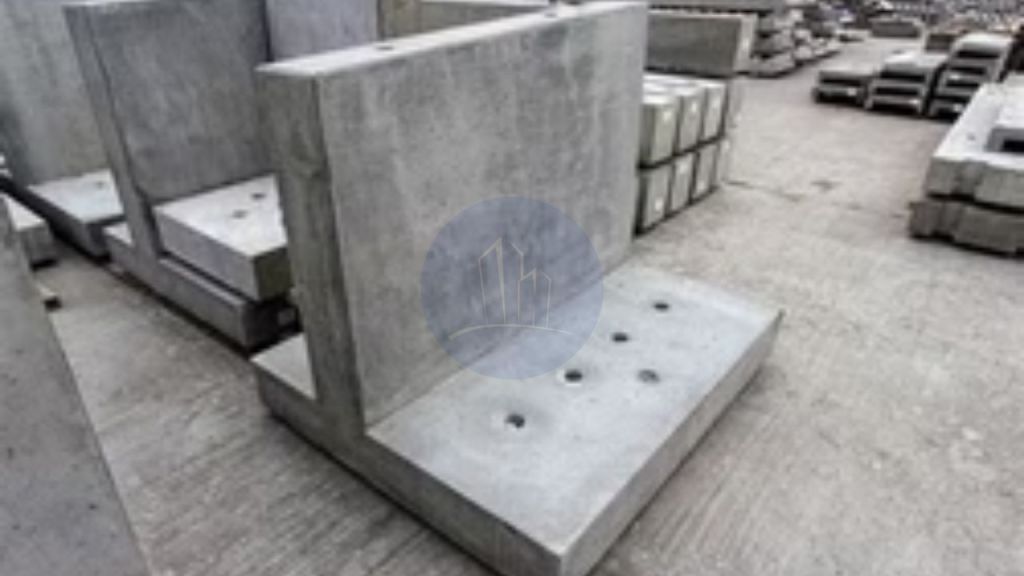
Cantilever retaining walls are the most common retaining wall type. They are reinforced concrete structures wherein the lateral earth pressure is countered by the cumulative action of total structural members.
Cantilever retaining walls consist of a stem, a base slab which is divided into toe slab and heel slab as shown in the figure.
The vertical stem wall is extended to the back fill side or heel side and is called a heel slab and the slab on the other side is a toe slab as shown in the figure.
The stem wall, toe slab, and heel slab act as cantilevers fixed injunction and spanning to other ends. The back filling of soil over the heel slabs imposes additional stability against lateral pressure and stabilises the wall against overturning and sliding.
The loads induced on various components
a) Heal slab and toe slab = Upward soil pressure from the bottom and tends to bend upward. Rebar is placed in a tension zone.
b) stem= Lateral earth pressure tends to bend in the opposite direction of back-fill.
These types of walls are economical and can be used for heights around 5-7 mtr. They are much lighter than gravity walls and require comparatively small foundations. These types of walls can be constructed as to cast in situ and precast and prestressed concrete depending on the site requirements.
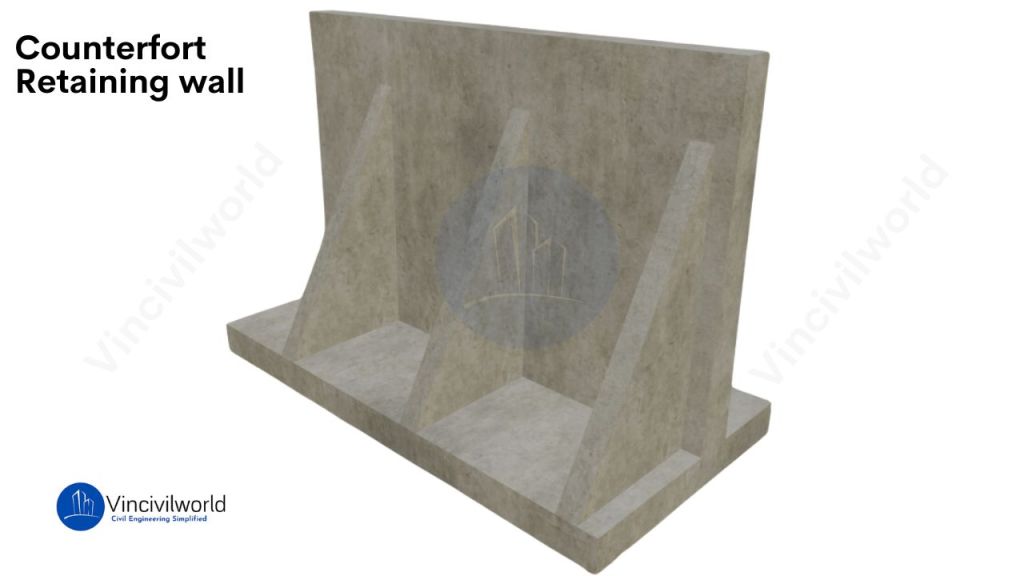
Counter-fort retaining walls
Counter-fort retaining wall is a cantilever retaining wall used when the height is around 7 mtr or more. For economising the structure, vertical bracing called counter-forts are provided on the back fill side. These counter-forts connect the heel slab and stem as shown in the figure. The stem and heel slabs between counter-fort act as continuous slabs and negotiate the high bending movements. The counter-forts function as tension stiffness and reduce the bending and shear stresses. These types of retaining walls are used for heights ranging from around 8-12 mtr.
Buttressed retaining walls
Buttress retaining walls have the vertical bracing located on the front side of the retaining wall in place of the back-fill side like that of counter-fort retaining walls. The structural action of the stem remains the same as the counter-fort walls.
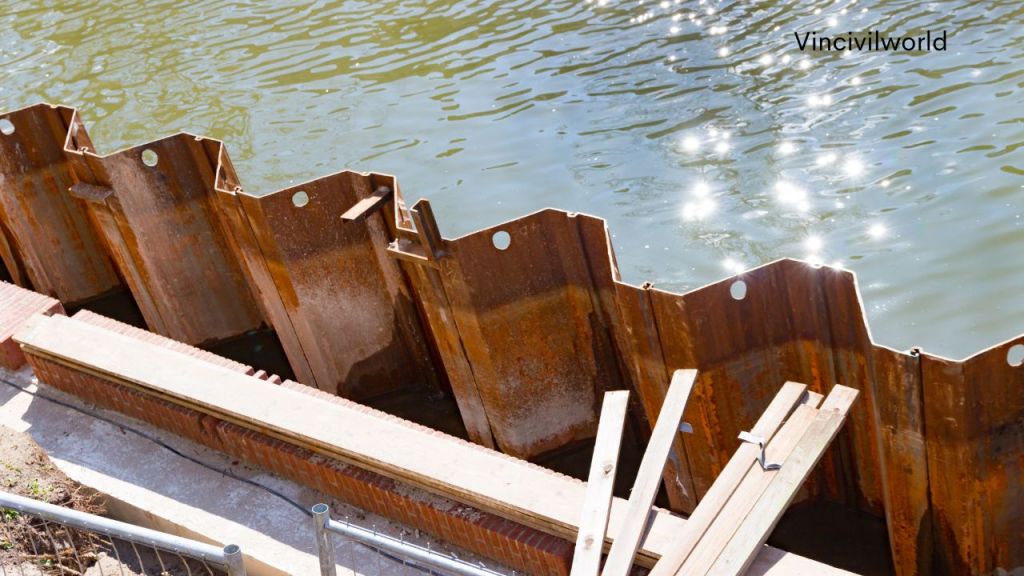
Sheet piled retaining walls
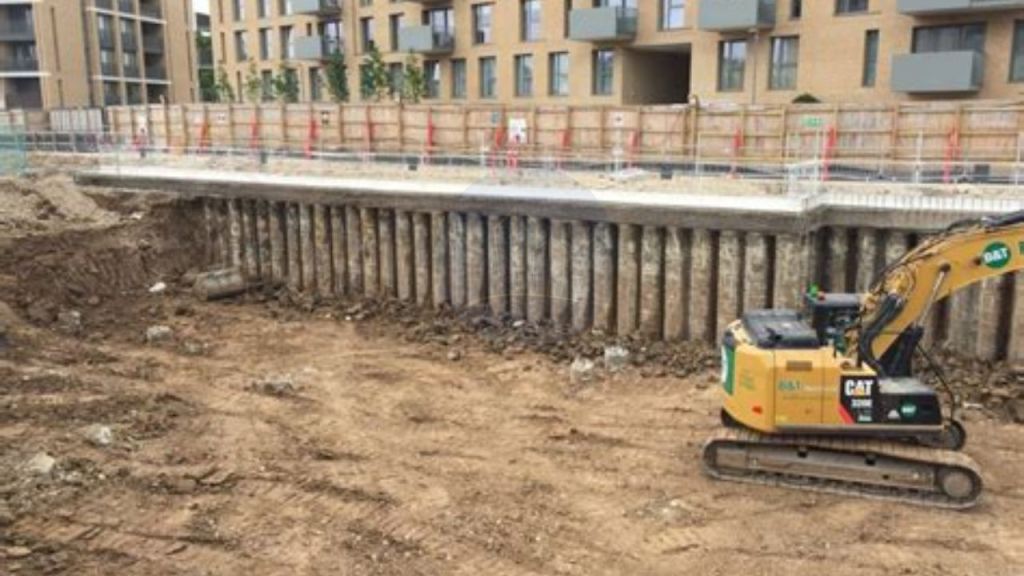
Sheet pile walls are erected using steel sheets into a slope to be protected or for excavations up to a required depth. Sheet pile retaining wall economical till a height of 6m and cannot negotiate huge loads. Sheet pile acts as a temporary wall that is driven into the excavation area for protecting the area from collapsing. They provide high resistance to driving stresses. They can also be reused and are considered the most economical retaining solutions. They can be bolted and driven easily and do not deform on driving. The problem with sheet piles is the noise it creates while driving.
Piled retaining walls
These types of retaining walls consist of a sequence of bored piles. The bored piled retaining walls are often accompanied by erection earth anchors, shot-creating the pile gaps, and provision of additional supports depending on the site conditions and designs. Bored pile retaining walls are used in areas where sheet pile tends to create a lot of noise and disturbs the areas.
These types of piles are used for temporary and permanent works. They can hold huge lateral pressure and are used for holding earth for high depth excavations without disturbing the nearby structures. Bored pile retaining walls are classified into contiguous pile walls, tangent pile walls & secant pile walls according to the sequence of piling works.
Anchored retaining walls
Anchored retaining walls, also known as tie-back systems, are essential structural components used in construction. They are mostly used to stabilize earth and as support structures. Anchored Retaining walls deliver lateral support to walls. They prevent soil from shifting or eroding. These walls are commonly used in applications like deep excavations, embankments, and hillside retention etc.