Bitumen for roads is an important topic to understand when it comes to road construction. Bitumen is used in road construction because of the wide range of features and advantages it possesses over other pavement construction materials. The significance of bitumen in the construction of roads will be demonstrated in this article. In addition, we shall see bitumen road layers, various bituminous materials, cutback bitumen, bitumen grade, and bitumen properties.
- Bitumen for roads – Bituminous binder types
- Desirable properties of bitumen- an important topic in bitumen for roads
- Bitumen for roads – Types of Bituminous materials
- Grade of bitumen for roads – Types and Uses
- Bitumen road layers
Bitumen for roads – Bituminous binder types
There are two types of bituminous binder for road construction.
- Bitumen (by distillation of crude oil)
- Tar (Produced from coal)
So, what are the difference between them?
Bitumen vs Tar – Comparison
The table below shows a comparison between tar and bitumen.
| Bitumen | Tar |
| Petrolium product | Distillation of coal or wood |
| Soluble in carbon disulphide and carbon tetrachloride | Soluble in toluene only |
| Temperature succeptibility is low | Temperature succeptibility is higher than bitumen |
| Free carbon content is less | Free carbon content is more |
Now, let’s sneak into the manufacturing of tar, being one of the important bituminous materials
Related posts from vincivilworld
Tar manufacturing
Generally, tar is made by heating coal inside a chemical apparatus. Most tar is produced from coal as a byproduct of coke production, but it can also be produced from petroleum, peat or wood.
The major steps in tar manufacturing are,
- Coal undergoes carbonation and produces crude tar
- Crude tar undergoes distillation/ refining and produces a residue
- The residue blends with distilled oil fraction and produces tar
I am going to tell more about the properties of bitumen now.
Also read: Classification of roads-5 types of roads full details
Desirable properties of bitumen- an important topic in bitumen for roads
The desirable properties of bitumen are,
- Viscosity of bitumen during mixing and compaction is adequate
- Bituminous material should not highly temperature and susceptible
- In presence of water the bitumen should not strip off from aggregate
- The adhesive property of bitumen binds together all the components without bringing about any positive or negative changes in their properties
- Bitumen is insoluble in water and can serve as an effective sealant
- Due to versatility property of Bitumen it is relatively easy to use it in many applications because of its thermoplastic property
- Bitumen play a vital role in distributing the traffic loads on the pavement to the layers beneath
Bitumen for roads – Types of Bituminous materials
Okay. So, what are the types of bituminous materials that are used in flexible pavement construction? Below is the list for you.
- Paving grade material
- Modified bituminous binder
- Cutback bitumen
- Bitumen emulsion
Among the list, cutback bitumen is the major. Let me tell you more details about cutback bitumen.
Cutback bitumen
Cutback bitumen is the bitumen the viscosity of which is reduced by a volatile diluent. It is used in low-temperature mixing.
Three types of cutback bitumen are available
- Rapid curing
- Medium curing
- Slow curing
The diluent while mixing varies with the type of cutback bitumen.
| Type of cutback bitumen | Diluent |
| Rapid curing | Nafthal, gasoline |
| Medium curing | Carosine or diesel oil |
| Slow curing | High boiling point gas oil |
Bituminous emulsion
A bitumen emulsion is a liquid product in which a substantial amount of bitumen suspended in a finely divided condition in an aqueous medium and stabilized by means of one or more suitable material
Three types of bitumen emulsions are available
- Rapid setting
- Medium setting
- Slow setting
Also read: Alignment of road: Factors affecting- obligatory points with figures
Grade of bitumen for roads – Types and Uses
To determine the grade of bitumen, penetration test is conducted. The results are expressed in 1/10 mm. When penetration value is represented as 80/1000, it is called grading of bitumen.
The old method of grading is viscosity test. Two viscosities kinematic and absolute and penetration value by penetration test results are collected. Based on this, bitumen is graded. The tables shows the grade of bitumen and values of viscosity in accordance with penetration.
| Grade of bitumen | Absolute viscosity | Kinematic viscosity | Penetration |
| VG 10 | 800 | 250 | 80- 100 |
| VG 20 | 1000 | 300 | 60- 80 |
| VG 30 | 2400 | 350 | 50- 70 |
| VG 40 | 3200 | 400 | 40- 60 |
Let me tell you the application of each of the grade of bitumen now.
VG- 10- Used in spray application since viscosity is very less
VG- 20- Used in cold area
VG- 30- Commonly used in India
VG- 40- High grade bitumen used in high traffic areas
Okay. So, lets’ learn about the bituminous layers.
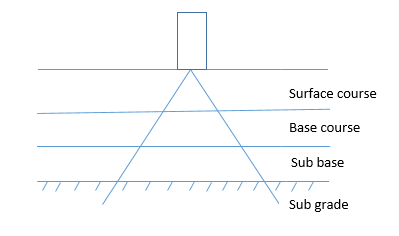
Bitumen road layers
Let’s first look into the road layers to understand bitumen road layers.
The bitumen road layers come in the surface layer shown in the figure above. The figure below shows that. Bituminous mix consists of aggregate and binder. Aggregate consists of coarse aggregate, fine aggregate and filler less than 0.075mm.
- Bituminous concrete consists of aggregate and bitumen.
- Thickness of base course depends on grading of aggregate
- Dense graded aggregates are provided in base course. That is the permeability will be very less
- Number of voids should be very less
- Dense bituminous macadam should be given as a binder course
So, the trip is over. Hope the time you spend for reading about the bitumen for road was worth it.
MUST READ: Road margins- 6 types of road margin in highway
Happy learning!