Best cement brands in India is a question that comes up frequently among homeowners, builders, and civil engineers planning durable construction projects. With rapid infrastructure growth and rising quality expectations, choosing the right cement has become more important than ever. Several factors influence this decision, including strength, consistency, durability, and performance under Indian site conditions. Today, many top cement companies in India offer a wide range of products designed for residential, commercial, and infrastructure works. Understanding best cement quality in India helps buyers make informed choices rather than relying only on brand names. People often ask which cement is best in India and look for reliable comparisons among the best cement brands in India. This article answers that question clearly by examining leading cement companies and their performance in 2025.
Which are the best cement companies in India? Which is the best cement in India? This is the common question every individual should be asking while deciding to go for home construction.
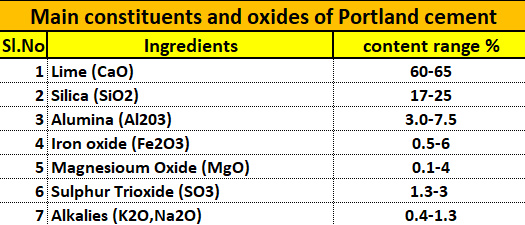
Cement is the most significant and widely used construction material which forms an integral part of any structure. Cement is the major ingredient of concrete and mortar and the structural stability and life of a structure or building depends on the cement quality.
- Significance of cement in construction sector
- Which is the best cement brand for your House/Structure?
- What is the difference between best cement company and best cement?
- Top cement brands in India in terms of Market share
- Ramco cements
- Conclusion
Significance of cement in construction sector
In large industrial, commercial, and residential projects, contract documents specify the best cement brand in India. They also clearly specify the cement type and list approved vendors. However, for individual home construction, decisions often rely on the engineer or contractor. Even so, homeowners should understand the best cement quality in India. They should also know the available cement types. It is essential for homeowners to identify which cement is best in India for their needs. Basic knowledge of leading brands is important. Understanding applications helps ensure durability, safety, and long-term performance. This is crucial when choosing from the best cement brands in India for residential construction.
Which is the best cement brand for your House/Structure?
After China, India is the second-largest cement producer globally. Production is expected to rise to around 453 million tonnes in FY25. It will expand further in FY26 due to strong infrastructure and housing demand. India’s installed cement production capacity is approximately 668–690 million tonnes per annum, with major clusters in South, North, and West India. The sector continues to grow, with planned capacity additions of 150–170 million tonnes by FY28. More than 200 large cement plants operate nationwide, and producers are investing heavily in expansion, sustainability, and efficiency. This article highlights the top 8 best cement companies in India based on production capacity, quality, and market presence in 2025.
What is the difference between best cement company and best cement?
The difference between the best cement company and the best cement often creates confusion. In reality, all reputed cement companies manufacture cement in accordance with prescribed Indian standards. Therefore, there is no absolute “best cement” or “best brand.” What mainly distinguishes the best cement companies in India is their production capacity, quality consistency, marketing strength, and wide distribution network. Regional availability plays a key role in cement selection, as a well-distributed brand ensures fresh supply and reliable performance. For most users, the choice of cement depends on local availability, application requirements, and budget rather than brand name alone. Therefore, this article lists leading cement companies based on market share and widespread availability across different regions of India.
Top cement brands in India in terms of Market share
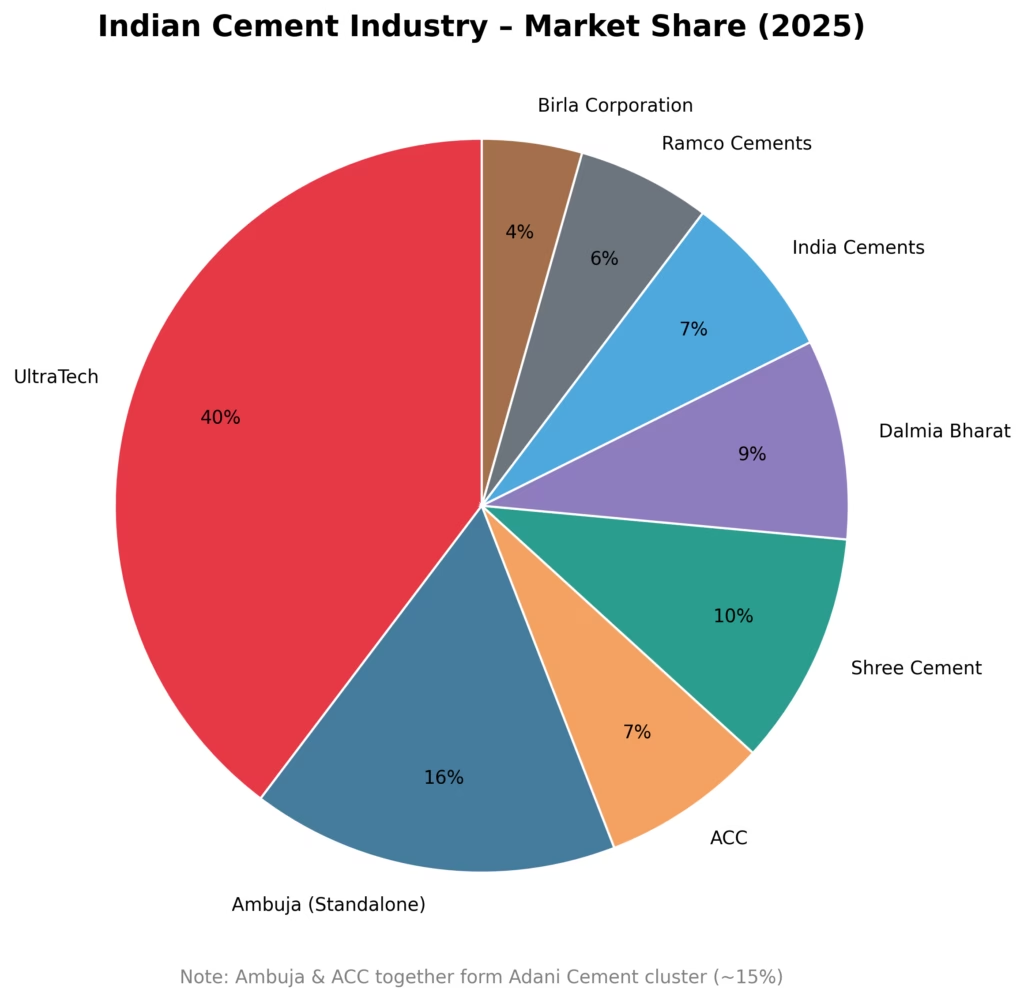
As per India Brand Equity Foundation (IFBL) Ultratech stand at first position in terms of market share and Market cap.
Let us go through the details of top cement companies in india in terms of market capitalization and market share
1.UltraTech – Best cement companies in India
Ultra Tech is the largest manufacturer of grey cement, white cement, and Ready mix concrete in India. It is the flagship cement company of the Aditya Birla Group. Established in 1983, UltraTech Cement boasts 23 integrated plants. It also operates 1 clinkerisation unit. Additionally, it runs 26 grinding units and 7 bulk terminals. The company manages 1 white cement plant, 2 Wall Care putty plants, and over 100 RMC plants. Ultratech is the third-largest company in the world (Excluding china) and has business operations in UAE, Bahrain, Sri Lanka, and India. Ultra Tech has a consolidated capacity of 116.8 million tonnes per annum (MT PA) of grey cement.

- Establishment: 1987 ✅
- Headquarter: Mumbai ✅
- Market share: ≈ 26–28%
- Market Cap (Rs Cr.): ₹3.1–3.3 lakh crore (≈ 30–32%)
- Production capacity: ≈ 183–185 MTPA
Ultratech production line includes Ordinary Portland Cement, Portland Blast Furnace Slag Cement, Portland Pozzolana Cement, etc. They are also leading producers of White Cement, Ready Mix Concrete, building products, etc.
2.Ambuja Cement – Best cement companies in India
Ambuja cement formerly known as (Gujrat Ambuja Cement Limited ) is the second-largest cement company in India in terms of the Market share. It was founded in 1983 and has their headquarter in Mumbai. Ambuja Cement got five integrated cement manufacturing plants and eight cement grinding units spanning across the country with a production capacity of 29.65 million tonnes per Annum (MT PA).
All Ambuja Cement plants are ISO 14001 certified. It is also plastic negative, by burning as much as over 75,000 tonnes of plastic waste in its kilns, equivalent to 2.5 times of total plastic used. The company also generated 7.1% of its power needs from renewable resources.
Ambuja Cement is known for its high strength, high performance Ordinary Portland Cement (OPC) and Pozzolana Portland Cement (PPC) and was the first to introduce 53-grade cement in the market.

Ambuja Cements (Adani Group) – UPDATED
(Include Ambuja + ACC + acquired assets context)
- Establishment: 1983 ✅
- Headquarter: Mumbai ✅
- Market share: ≈ 10–11% (standalone Ambuja)
- Market Cap (Rs Cr.): ₹1.2–1.4 lakh crore
- Production capacity: ≈ 75–80 MTPA
- 📌 Note: Along with ACC, Adani Cement cluster controls ≈ 14–15% of India’s cement market.
In 2005, Ambuja Cements (as the company was known then) joined the reputed Holcim Group of Switzerland. Another premier Indian cement company, ACC Limited, also became part of this group. Later, in 2015, Holcim Limited and Lafarge SA came together in a merger of equals to form LafargeHolcim – the new world leader in building materials.
3.ACC Cements – Best cement companies in India
It is formerly known as an Associate Cement Company is one of the oldest and leading manufacturers of cement and ready mix concrete. ACC Cement was established in the year 1936 with headquarter in Mumbai and having 17 cement manufacturing units, over 90 ready mix concrete plants etc.
ACC Cement – UPDATED
- Establishment: 1936 ✅
- Headquarter: Mumbai ✅
- Market share: ≈ 4–5%
- Market Cap (Rs Cr.): ₹40,000–45,000 crore
- Production capacity: ≈ 36–38 MTPA
In 2005, ACC became part of the Holcim Group of Switzerland. Subsequently, in 2015, Holcim and Lafarge came together in a merger to form LafargeHolcim – the global leader in building materials and solutions.
4.Shree cements – Best cement companies in India
SCL is one of the fast growing cement companies in India. Shree Cement was Incorporated in 1979 by renowned Bangur family based out of Kolkata and first cement plant was established in the year 1985.
SCL is one of India’s Top five cement producers and among the fastest growing cement companies with an installed capacity of 45 Million Tonnes Per Annum in India and 50-55 MPTA including overseas.
Shree Cement – UPDATED
- Establishment: 1979 ✅
- Headquarter: Kolkata ✅
- Market share: ≈ 6–7%
- Market Cap (Rs Cr.): ₹95,000–1,05,000 crore
- Production capacity: ≈ 50–55 MTPA (India + overseas)

SCPL is known for delivery of good quality products at an affordable price range.
Dalmia cement
They are one of India’s pioneering homegrown cement companies established in 1939 having headquarter in Delhi. Dalmia Cement (Bharat) Ltd, which is a 100% subsidiary of Dalmia Bharat Ltd.
The company has a production capacity of 30.75 MP TA and operates thirteen cement plants and grinding units which are spread across nine states. Dalmia Cement is the only company with at least one plant in each of the four key eastern states of West Bengal, Bihar, Jharkhand, and Odisha.
- Establishment: 1939 ✅
- Headquarter: Delhi ✅
- Market share: ≈ 5–6%
- Market Cap (Rs Cr.): ₹35,000–40,000 crore
- Production capacity: ≈ 44–46 MTPA
Dalmia is the largest manufacturer of slag cement and is a leader in super-speciality cement for oil wells, railway sleepers, and airstrips. These brands are available as Portland Pozzolana Cement, Portland Slag Cement, Composite Cement, and Ordinary Portland Cement in select markets
Birla Corporation
Birla Corporation is a flagship company of MP Birla group and got 10 cement plants at various locations and having a production capacity of 15.5 MT PA. Incorporated as Birla Jute Manufacturing Company Limited in 1919 Birla corporation is engaged in the manufacture of cement. They manufacture varieties of cement like Ordinary Portland Cement (OPC), 43 & 53 grades, Portland Pozzolana Cement (PPC), fly ash-based PPC, Low Alkali Portland Cement, Portland Slag Cement (PSC), Low Heat Cement and Sulfates Resistant Cement.

- Establishment: 1946 ✅
- Headquarter: Chennai ✅
- Market share: ≈ 2–3%
- Market Cap (Rs Cr.): ₹7,000–8,000 crore
- Production capacity: ≈ 14–15 MTPA
The company acquired 100% shares of Reliance Cement Company Private Limited for a value 4800 crores. The total capacity including acquisition stands at 15.5 MT PA.
India Cements
India cements Ltd was founded in the year 1946 by Shri S N N Sankaralinga Iyer and Sri T S Narayanaswami. From a two plant company having a capacity of just 1.3 million tonnes in 1989, India Cements has robustly grown in the last two decades to a total capacity of 15.5 million tonnes per annum. India Cements has now 8 integrated cement plants in Tamil Nadu, Telangana, Andhra Pradesh and Rajasthan and two grinding units, one each in Tamil Nadu and Maharashtra.
- Establishment: 1946
- Headquarter: Chennai
- Market share : 5%
- Market Cap (Rs Cr.) Rs. 6047Cr. (1.22%)
- Production capacity : 15.5 MTPA
Ramco cements
Ramco Cements Limited is the flagship company of the Ramco Group, a well-known business group of South India. having their head quarters in Chennai. It is eight in the list of top 10 cement company in India

The main product of the company is Portland cement, manufactured in eight state-of-the-art production facilities that include Integrated Cement plants and Grinding units with a current total production capacity of 16.45 MTPA. The company is the fifth largest cement producer in the country.
- Establishment: 1946 ✅
- Headquarter: Chennai ✅
- Market share: ≈ 3–4%
- Market Cap (Rs Cr.): ₹25,000–28,000 crore
- Production capacity: ≈ 23–25 MTPA
Key Takeaways
- Choosing the best cement brands in India is crucial for durable construction projects due to factors like strength and performance.
- The article highlights leading cement companies based on market share and production capacity as of 2025.
- UltraTech and Ambuja Cement rank among the top cement companies in India, with significant market shares and production capacities.
- The difference between best cement companies and the best cement often lies in production capacity and local availability.
- Homeowners should prioritize readily available brands with good marketing networks for their construction needs.
Conclusion
All cement companies manufacture their products in compliance with Indian Standards (IS) and relevant international standards, ensuring consistent quality and performance. Therefore, there is no single answer to which cement is best in India, as most leading brands meet the required technical specifications. While selecting the best cement brand in India, availability in the local market, logistics, and budget play a major role. The top cement companies in India listed in this article stand out mainly due to their large manufacturing capacity, strong distribution network, and wide regional presence. However, many other best cement brands in India also offer excellent strength, durability, and reliability. Builders and homeowners can confidently choose any standard-compliant cement that is easily available nearby, as best cement quality in India is maintained across reputed manufacturers.