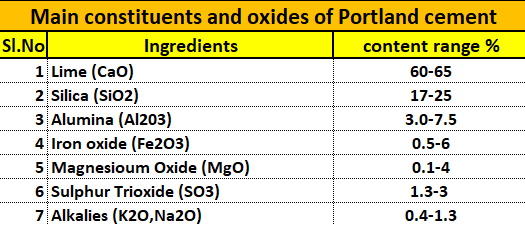
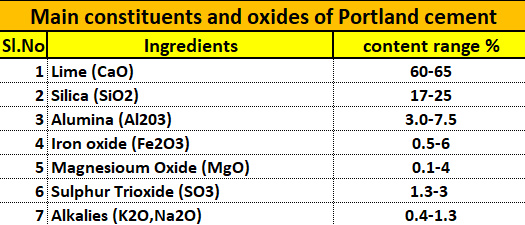
Tests on bitumen are essential for ensuring the quality and durability of flexible pavements and other civil engineering structures. Bitumen is a viscous, binding material used in construction. Various lab tests confirm its properties. This article delves into the comprehensive set of tests on bitumen that civil engineers and researchers perform to ensure the material’s suitability. We will explore key assessments. These include the softening point test, the penetration test, the ductility test, and the viscosity test on bitumen, among others. Understanding these bitumen tests is crucial for guaranteeing high-quality construction and prolonging the life of road surfaces.
Bitumen is a binding material extensively used in the construction of flexible pavements, damp-proofing of the basement, floors, waterproofing of roofs, corrosion protection of reinforcement structures, etc. The bitumen is viscous black or brown mixture of hydrocarbons obtained as a byproduct on refining crude petroleum.Bitumen is responsible for imparting quality and durability for flexible pavements and is necessary to confirm its quality before applications. This article is about the various lab tests and procedures performed on bitumen for ensuring the quality.
Properties of bitumen
The properties of bitumen are fundamental to its use in construction, determining its quality and performance. To ensure a durable material, these characteristics are confirmed through rigorous testing.

Key Properties of Bitumen
- Consistency: Bitumen must maintain its physical state across a wide temperature range. It should stay firm in heat. It should also avoid brittleness in cold.
- Viscosity: Its resistance to flow is crucial for proper mixing with aggregates and effective compaction during the paving process.
- Adhesiveness: The material must possess strong binding properties. It should create a lasting bond with aggregates. This ensures the structural integrity of the pavement.
- Durability: Bitumen should be resistant to aging and weathering to retain its properties and prolong the lifespan of the finished structure.
Tests on bitumen
To ensure the quality and durability of bitumen for construction, technicians perform a series of standardized laboratory tests on bitumen. These tests evaluate its key properties and characteristics.
- Softening point test
- Flash and fire point test
- Solubility test
- Viscosity test
- Distillation test
- Water content test
- Ductility test
- Penetration test
- Specific gravity test
Softening Point Test on bitumen
Softening point test indicates the point at which bitumen attains a particular degree of softening under standard test conditions. The test helps in determining the consistency of bitumen and done using ring and ball test apparatus.
Ring and ball test apparatus include a brass ring, steel ball, water bath, and thermometer as shown in the figure.

Test procedure
- Firstly, heat the sample at a temperature of around 75 to 100-degree wherein the bitumen transforms to a liquid state.
- The brass ring is heated before placing inside the mercury-coated metal plate. Glycerine is applied over the ring to prevent sticking.
- Then fill the brass ring with molten bitumen and cool it for 30 minutes. Trim the excess material using a knife.
- After filling assemble the apparatus and place the balls over the top of the specimen sample.
- Then fill the apparatus with boiled distilled water. However, the height of filling should be 50mm above the topmost surface of the ring.
- After that heat the water bath at a rate of 5-degree Celsius per minute.
- On heating, the bitumen softens and the ball slowly sinks and touches the bottom plate.
- Finally, note down the temperature at which the specimen touches the lower plate and this temperature is the softening point of the bitumen specimen.
Normally the softening temperature varies from 35 degrees to 70 degree Celsius.
Flash and fire point test
Flash-point test refers to the temperature at which the specimen becomes volatile and catches fire under test conditions. The apparatus for the flash and fire point test is Pensky – Morten’s closed cup apparatus.
Procedure
- Initially , fill the bitumen sample up to the filling mark and close the apparatus.
- Then, fix the thermometer in a proper position as shown in the figure.
- Heat the specimen at a rate of 5-degree Celsius per minute.
- Then, constantly keep stirring the specimen and apply the test flames at regular intervals.
- The temperature at which the flame produces a light flash inside the cup is the flash point.
- On further heating, the bitumen specimen inflames and catches fire and this temperature is the fire point.

Solubility Test
The solubility test determines the purity of bitumen. Lot of impurities like carbon, salts, etc gets entrapped in bitumen and hamper the quality . Hence this test is necessary for calculating the impurity percentage.

- Firstly, dissolve the sample in carbon disulfide.
- Then filter the solution using a porosity filter.
- Finally, calculate the percentage of impurity from the residue left.
Penetration test on bitumen
The penetration test measures the hardness or softness of the bitumen. A penetrometer is an apparatus used for computing penetration tests which consist of a needle that weighs 100 gms. Similarly, penetration readings are measured in terms of mm/10.
Procedure
- Firstly, heat the specimen into pouring consistency and immerse the specimen in the water bath. However, make sure the temperature is around 25-degree Celsius.
- After half an hour, take-out the specimen and place it below the apparatus.
- Meanwhile, adjust and set the dial to zero reading and allow the needle to fall on the specimen.
- Immediately, measure the penetration depth.
- Then repeat this process a minimum of three times and note down the values. The average values
The penetration value ranges from 20 to 225. Low penetration values represent good quality bitumen.
Viscosity test on bitumen
The viscosity of bitumen is the measure of the resistance of the fluid to flow. The unit of viscosity is seconds. Too High or low viscosity impacts the compaction, penetration, lubrication, and coating capacity over aggregates. A viscometer apparatus is for finding the viscosity.
Procedure
- Prepare the specimen under standard temperature.
- Further, Level the cup with the help of the bubble level.
- Then heat the water bath at a constant temperature.
- Next, clean the receiver and pour the specimen up to 20ml.
- Allow the bitumen to pass through the orifice. Open the valve.
- Start the stopwatch and note down the time at which it reaches 25ml.
- Then repeat the test three times and calculate the mean value of viscosity.
Distillation test or loss of heating test
The distillation test determines the quantity and nature of volatile elements in bitumen. Through this test, volatile and non-volatile components are separated.

- Initially, take 200 grams of bitumen and Note down the weight of the sample.
- Next, continuously heat the sample at 360-degree Celsius for 15 minutes.
- After that, carefully distil the sample in a 500ml distillation flask.
- Measure the residue left. This is the actual quantity of bitumen.
Water content test on bitumen
In a good quality bitumen, the water content should be minimum. Because excess water content produces foam when heated above the melting point.
- Initially,the bitumen sample is weighed using a weighing machine.
- Next step is to immerse the sample in pure petroleum which is free from water.
- After immersing, immediately start heating the specimen and distill the water.
- Then condense the distillate and collect the condensed water at the bottom.
- Record the weight of residue

The water content is the weight of condensed water to the weight of the sample. However, for good quality bitumen water content should not exceed 0.2 percent by weight.
Ductility test on bitumen
The ductility is the ability to undergo deformation or elongation under load. Ductility is measured as the distance in centimeters to which a standard specimen of bitumen will elongate without breaking. The ductility value ranges from 5 to 100 cm. However, the minimum ductility value should be 73 mm as per BIS.

- Initially, heat the specimen into pouring consistency.
- Then, allow them to cool for 30 minutes and remove the excess specimen using a knife.
- After that, take the sample specimen in the form of a standard briquette.
- Continue to keep the specimen assembly in a water bath for 90 minutes, however maintaining the temperature to 27- degrees Celsius.
- After hooking the clips in the ductility machine, start applying the load and allow them to stretch.
- Finally, record the reading on the scale at which the bitumen breaks.
Specific gravity test on bitumen
Specific gravity is the ratio of the weight/mass of the bitumen specimen with equal mass of water at 27-degree Celsius. Normally the specific gravity of bitumen ranges between 0.97 to 1.02. The apparatus to determine specific gravity is a pycnometer.
The formula for specific gravity is
Specific gravity = (W3-W1)/[(W3-W1)-(W4-W3)]
Where, W1 – Weight of empty pycnometer
W2 – Weight of pycnometer with distilled water
W3 – Weight of pycnometer with half-filled bitumen
W4 – Weight of pycnometer with half-filled bitumen and distilled water

The test procedure is as follows.
- Firstly, clean and dry the pycnometer. Make sure it contains no water.
- Then weigh the empty pycnometer and mark it as W1.
- Then ,empty the apparatus and again fill it with fresh distilled water.
- Similarly, weigh the pycnometer and record it as W2.
- Again empty and fill half of the apparatus with melted bitumen. Avoid the inclusion of air in the sample.
- Then allow the sample bottle to stand for 30 minutes. Similarly weigh the sample and mark it as W3.
- Now fill the rest with distilled water. Again, weigh the specimen. This is W4.
- Finally, determine the specific gravity using the formula.
Key Takeaways from Bitumen Tests
- Quality Control is Key: Standardized laboratory tests on bitumen are essential for quality control in civil engineering. They ensure that the material used in flexible pavements and other structures meets specific performance criteria, which is critical for long-term durability.
- Properties and Performance: Tests directly evaluate key properties of bitumen. These include its consistency, like softening point and penetration. They also assess resistance to flow, such as viscosity, and check purity, like solubility. These characteristics dictate how bitumen will behave during mixing, paving, and over its service life.
- Critical Assessments: Each test provides a unique insight. The softening point determines temperature stability, while the penetration test measures its hardness. The ductility test assesses its ability to stretch without breaking. This is a vital property for resisting cracking. The solubility test ensures it’s free from harmful impurities.
- Safety and Suitability: Tests like the flash and fire point are crucial for safety during handling and processing. The specific gravity test is used to accurately classify the bitumen. It also determines its correct proportion in asphalt mixes. Together, these tests guarantee the material’s suitability for construction.
Conclusion
The comprehensive suite of tests on bitumen is a fundamental practice in civil engineering. It serves as the backbone for ensuring the quality and durability of flexible pavements. It also supports other essential structures. Each assessment—from the softening point and penetration tests that characterize its physical state to the ductility and viscosity tests that measure its performance under stress—provides critical data points. This rigorous laboratory testing regimen is not merely about meeting standards. It guarantees that bitumen can withstand environmental extremes. It ensures bitumen can handle heavy traffic loads and the inevitable effects of aging. By confirming the material’s consistency, adhesiveness, and purity before it is ever used in a project, civil engineers can significantly prolong the lifespan of road surfaces and infrastructural assets, thereby building safer and more sustainable public works. Ultimately, these tests are indispensable for effective quality assurance in modern construction.