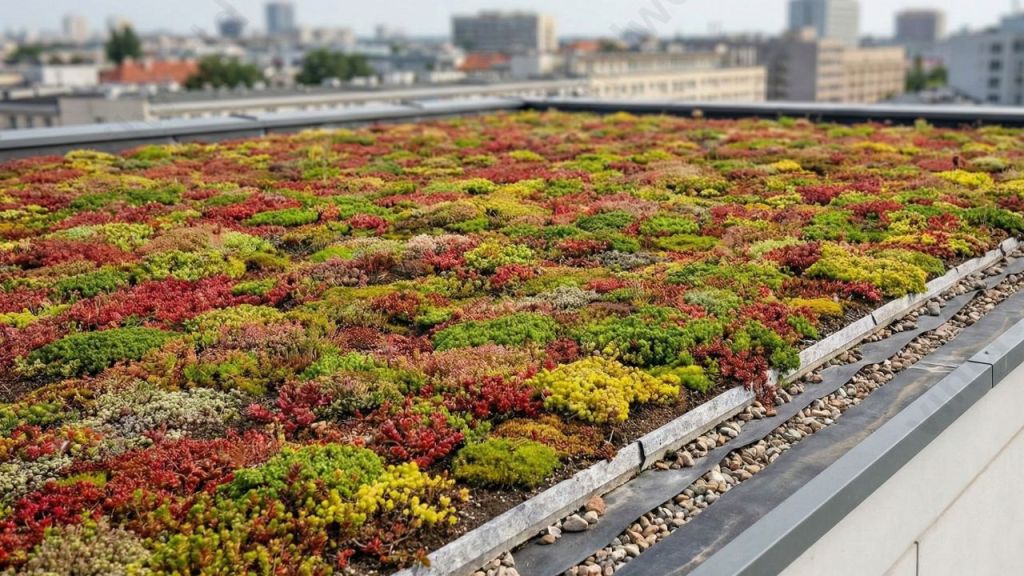
Green roof systems are innovative building solutions that integrate vegetation layers over rooftops to improve environmental and building performance. These systems are widely adopted in sustainable construction. They vary based on design, depth, and usage. It is important to understand the types of green roofs available today. In modern construction, green roofs in buildings help reduce heat gain, manage stormwater, and enhance urban biodiversity. From a design perspective, proper green roof construction ensures structural safety, drainage efficiency, and long-term durability. The key features of green roofs include waterproofing layers, insulation, growing media, and plant selection. When implemented correctly, the green roof advantages extend to energy savings. They also improve air quality and reduce the urban heat island effect. Additionally, they enhance aesthetic value, making them an effective solution for sustainable and resilient buildings.
Green roofs or Eco roofs have become the latest design trend in almost all buildings. A green roof, also known as a living roof, is a building’s roof that is covered in vegetation and a growing medium. This is because of its wide variety of benefits ranging from energy conservation to carbon sequestration.
In this blog, I will show you the full details about green roof systems, their types, components, merits and demerits. By the end of this article, you would be planning to install a green roof in your home or office. Ready for the journey through green roofs?
- What are Green Roof systems in Buildings ?
- Different Types of Green Roofs
- Green Roof System Construction Components
- Green Roof Advantages
- Green Roof Disadvantages
- Key Takeaways
- Conclusion
What are Green Roof systems in Buildings ?
Green roof systems in buildings are sustainable roofing solutions where vegetation is installed over a layered roof structure. These systems typically include waterproofing, drainage, insulation, growing media, and selected plants. Green roof systems help reduce heat gain, manage stormwater runoff, and improve thermal performance of buildings. They also enhance air quality, reduce noise pollution, and support urban biodiversity. Commonly used in residential, commercial, and institutional buildings, green roof systems contribute to energy efficiency and environmental sustainability. By lowering indoor temperatures and protecting roof membranes, green roofs increase roof lifespan while promoting eco-friendly and climate-resilient building design.Additional layers, such as a root barrier, drainage, and irrigation systems, can be used. Green roofs with rooftop ponds are another form of green roof that is used to treat grey water.

Different Types of Green Roofs
Different types of green roofs are classified based on vegetation depth, structural load, and maintenance needs. Understanding these types helps designers choose the right system for performance, cost, and sustainability in buildings.
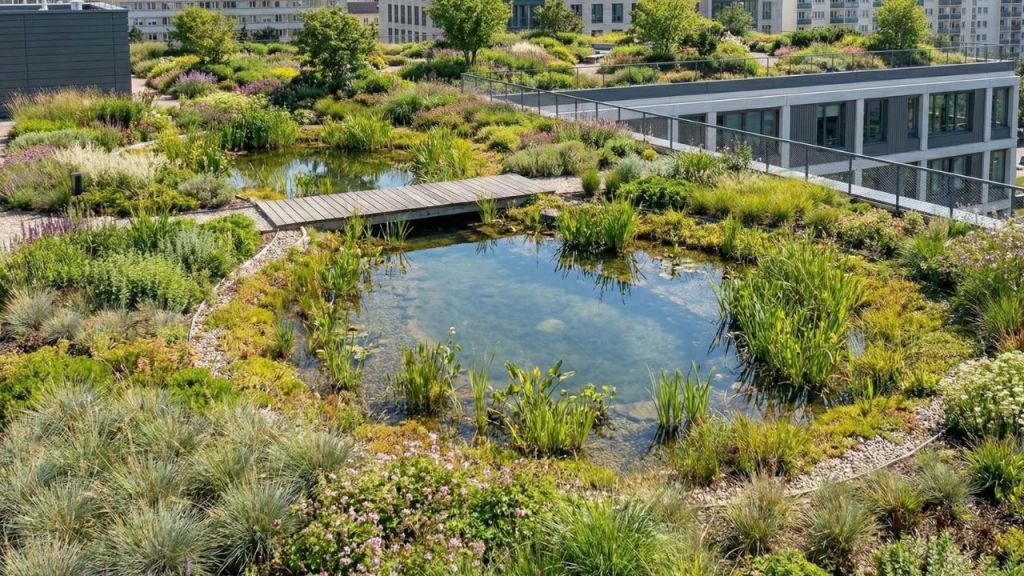

Types of Green Roofs
- Blue-Green Roofs
- Extensive Green Roofs
- Intensive Green Roofs
- Semi-Intensive Green Roofs
- Biodiverse (Brown) Roofs
Also Read : Green walls – Types and advantages
Blue-Green Roofs
Blue-Green Roofs combine green roof vegetation with integrated water storage systems to manage stormwater effectively. These roofs temporarily store rainwater, release it slowly, and support plant growth, reducing flooding risk and improving urban climate resilience.
Features of Blue-Green Roofs
- Integrated rainwater storage layer
- Controlled water release system
- Vegetation adapted to wet conditions
- Improved stormwater management
- Reduced urban flooding and runoff
Extensive Green roofs
- Extensive green roofs are a common choice among homeowners.
- They are light, low-maintenance, and do not need additional watering unless there is a prolonged drought.
- Designers can use them on flat roofs of both existing and new roof decks.
- Extensive green roofs typically feature an attractive vegetation layer about 80–150 mm thick, consisting of grass, moss, sedum, or small flowering plants.
Intensive Green Roofs
- Intensive green roofs support larger plants, typically 8–12 inches tall, including bushes, small trees, and a wider variety of vegetation. They are commonly known as roof gardens.
- To sustain this much thicker vegetation layer, they need a layer of rising medium/soil.
- They’re more popular in larger commercial ventures, such as parks and gardens.
- Intensive roofs require a much deeper substrate, which increases structural load and irrigation needs.

Semi-extensive Green roofs
Semi-extensive green roofs are hybrid systems that combine features of extensive and intensive roofs. They offer moderate vegetation depth and improved aesthetics. These roofs also have balanced maintenance requirements for residential and commercial buildings.
Features of Semi-Extensive Green Roofs
- Moderate irrigation and maintenance needs
- Moderate substrate depth
- Supports grasses, herbs, and small shrubs
- Medium structural load requirement
- Better insulation than extensive roofs
- Let me show you the components of a green roof.
Green Roof System Construction Components
You must install a green roof system for a green roof to develop and prosper. A green roof system is made up of many layers, which are as follows:
- Waterproofed roof deck
- Root-barrier security
- Membrane for Drainage
- Geotextile filter / filter layer
- Substrate / growing medium for green roofs
- Plants and trees
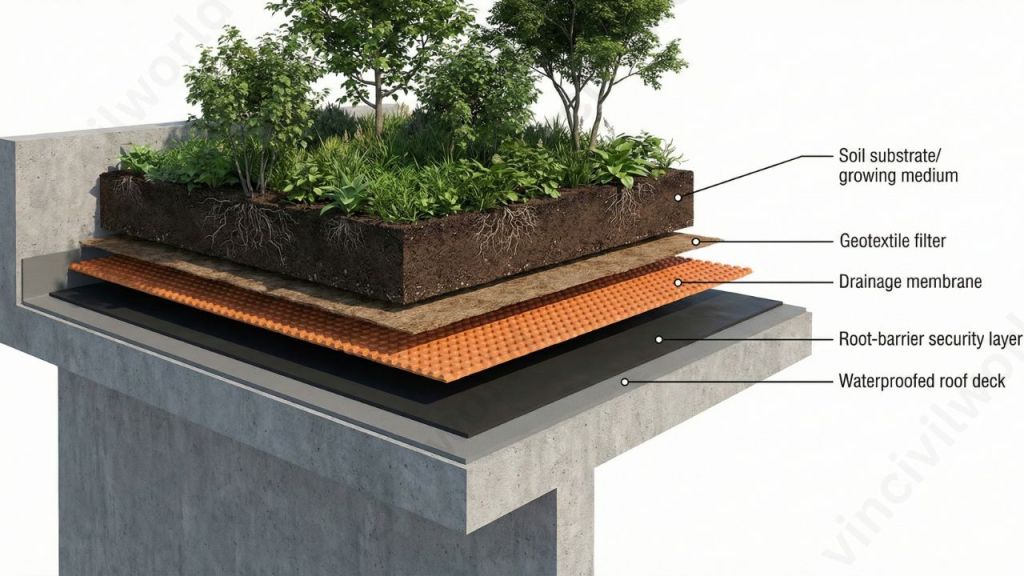

Let’s take a look at each one separately:
Waterproofed roof deck
Your roof deck may already have a waterproofing layer since waterproofing is an important part of the structure’s protection. If not a bitumen membrane or coating, asphalt on a shed, or any kind of liquid waterproofing may be used.
Also Read : Types of water proofing – 5 methods explained
Root barrier
- To avoid any roots from causing damage to the structure, a root barrier should be installed above the primary waterproofing layer.
- There are typically thin polyethylene plastic membranes.
- They are spread over the waterproofing layer and taped together.
- Root barriers are imperative in intensive roofs due to the potential for more woody and robust roots.
Membranes for Waterproof Drainage
- Rain and stormwater are dealt with by the drainage layer of a green roof system.
- It allows water to safely flow away from the roof into guttering and downpipes.
- It protects the structure as well as the plants from saturation and root damage by coping with excess water.
- The stud profile on these green roof drainage membranes helps to ensure proper drainage.
Filter Layer
The filter layer on a green roof prevents dirt, other substrates, and debris from clogging the drainage membrane’s cavities.
Growing Substrate
The substrate should be light, helps with drainage but is still absorbent enough to maintain enough water to sustain your plants’ growth. The commonly used substrates are:
- Bricks
- Aggregates
- Compost
- Medium clay soils
- Volcanic rocks such as lava and pumice
All of them offers the advantage of being all-natural and environmentally friendly.
Green Roof Advantages
- Green roofing has a longer life since a green coating protects it from UV radiation, snow, and ice.
- The roofing will last two to three times longer than a conventional roof because it will not be exposed to extreme high and low temperatures.
- It will be comfortable and cool inside during the summer and comfortably warm during the winter.
- Energy costs will be reduced as a result of the lower HVAC energy demands.
- The green roof especially the substratum absorbs both impact and environmental noise, such as rain and hail.
- Some of the invisible pollution and particles are filtered out of the air by plants.
- The pollution level in the air above gardens and parks is up to 80% lower than in the rest of the city.
- The vegetation layer, the substratum, and the irrigation layer filter and absorb 30 to 50 percent of rainwater, resulting in far less water in the sewage system.
- Green roofs help to increase the city’s fauna, such as butterflies, pollinating insects, and birds, among other things.
Green Roof Disadvantages
There are only a few drawbacks, with installation cost being the most significant. A green roof costs more to build than a conventional flat roof because builders must reinforce the underlying structure to handle the additional load.
That’s it about green roofs. Hope this blog motivated you to set up a green roof in your building. Let’s go green. Let’s adopt green roofs.
Key Takeaways
- Green roof systems integrate vegetation layers over rooftops to improve environmental and building performance.
- They play a major role in sustainable and climate-resilient construction.
- Understanding the types of green roofs helps in selecting suitable systems based on load, maintenance, and usage.
- Green roofs in buildings reduce heat gain, improve thermal comfort, and lower energy consumption.
- Proper green roof construction ensures effective waterproofing, drainage, and long-term durability.
- Key features of green roofs include insulation layers, drainage membranes, growing media, and plant systems.
- Green roofs support stormwater management and urban biodiversity.
- Noise reduction and air quality improvement are added benefits.
- Structural assessment is essential before installation.
- Overall, green roofs enhance sustainability and building lifespan.
Conclusion
Green roof systems offer an effective solution for creating sustainable, energy-efficient, and environmentally responsible buildings. By understanding the types of green roofs, designers and homeowners can choose systems that suit structural capacity, maintenance needs, and functional goals. The adoption of green roofs in buildings helps reduce heat gain, manage stormwater, and enhance urban biodiversity. Proper green roof construction is essential to ensure waterproofing, drainage efficiency, and long-term performance. The key features of green roofs include insulation layers, drainage membranes, and growing substrates. These elements contribute to improved thermal comfort and durability. With multiple green roof advantages, including energy savings, noise reduction, and extended roof lifespan, green roofs represent a practical and future-ready solution for sustainable building design.