Selecting the materials for the false ceiling is one of the tricky tasks everyone should be facing while thinking of a new construction or renovating an old one. The materials for false ceilings should be durable and be in line with the requirements of application areas.
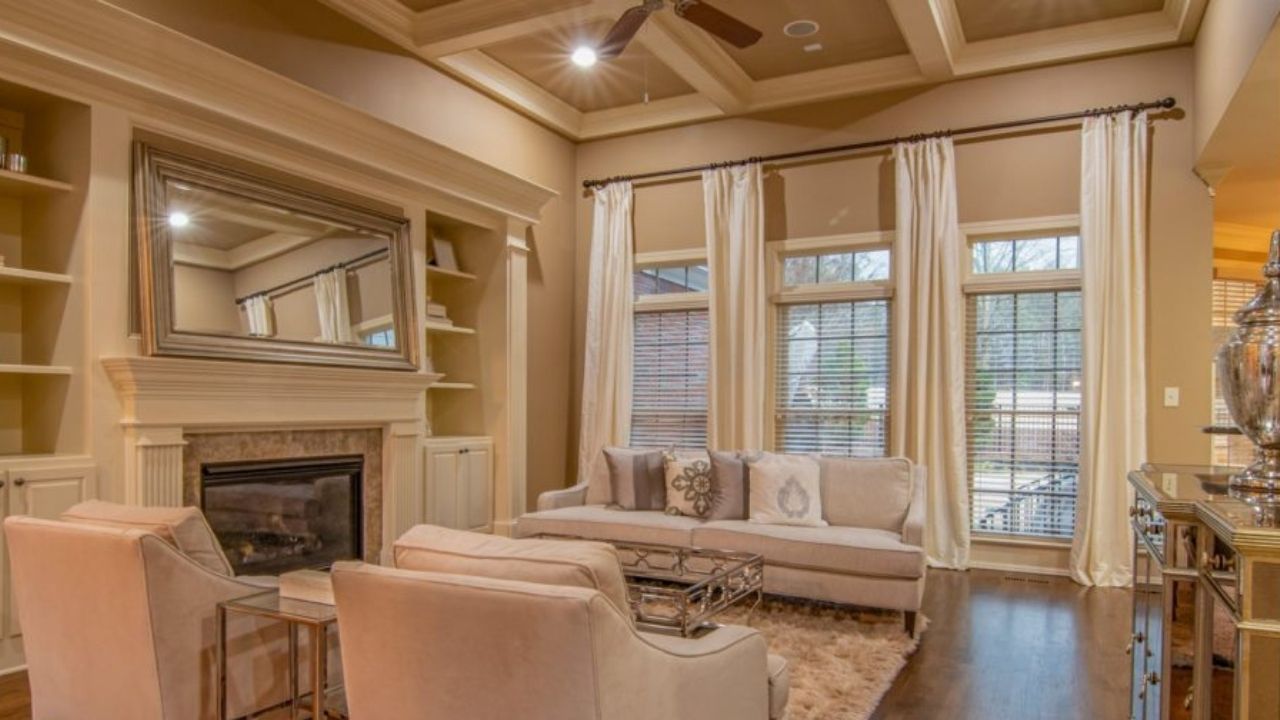
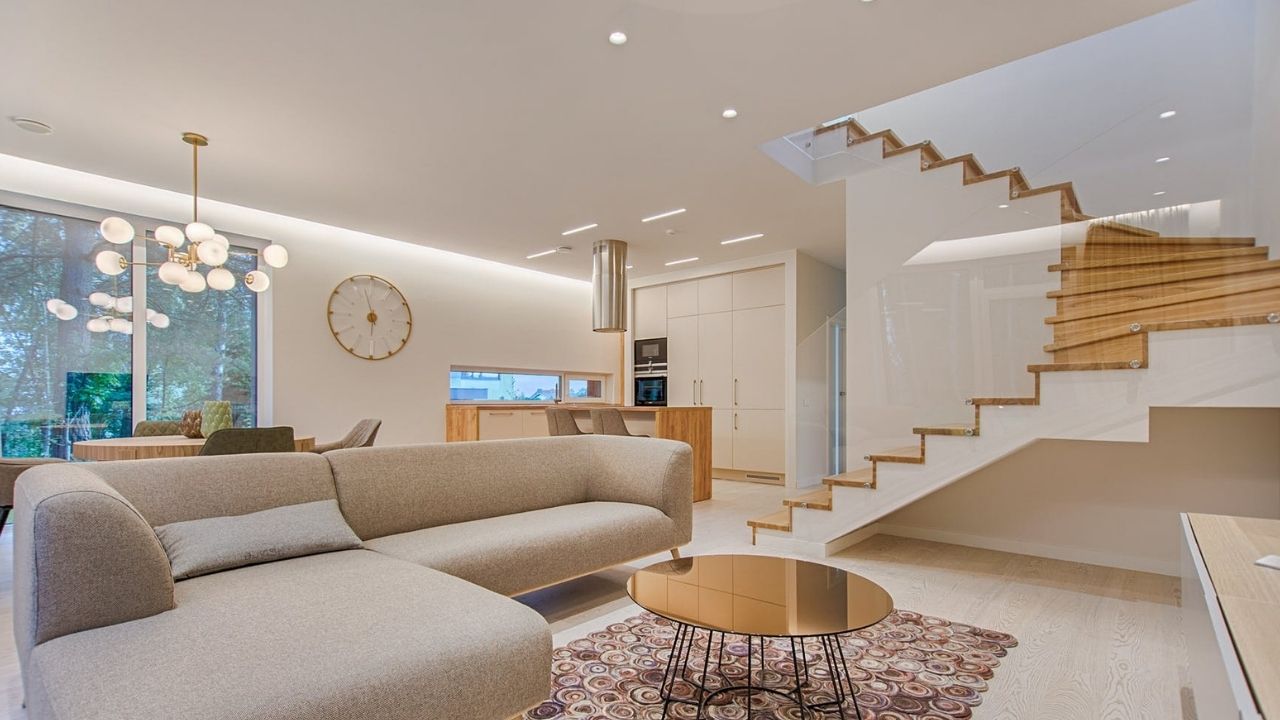
An artificial ceiling below the main roof of a room or a building is known as a false ceiling. False ceilings are second layer roofs, hanging from the main roof on suspended hanger supports. False ceilings provide an attractive and aesthetically pleasing look on the roofs. This article is about the top 7 trending materials for false ceilings.
- Benefits of False Ceiling
- Materials for False ceiling
- POP of Plaster of Paris False ceiling
- Gypsum board false ceiling
- Metal False ceiling (Tile and plant type)
- Wooden Ceiling
- PVC False Ceiling
- Mineral Fibre Board
- Disadvantages of false ceiling
- Installation method of all false ceilings
- Precautions For False ceiling works
Benefits of False Ceiling
The main benefits of false ceilings are…
- Improves the aesthetic appearance of the interiors.
- Reduces room height proportionally and makes space feel more compact and pleasant.
- Acts as heat insulators and thereby reduces air conditioning load. The air gap between the ceiling and roof behaves like a nonconducting medium and minimises the heat and cold transmission. This reduces the air conditioning loads and energy bills.
- A false ceiling hides the air condition ducts, fire sprinkler lines, and wiring for concealed light systems. It also conceals other security systems. This setup gives an excellent look to the ceilings.
- Helps accommodating additional ceiling lights. Ceiling lights in the right places enhance ambient lighting inside the room considerably.
- Acts as an acoustic insulator and a noise reduction medium (mainly uses in auditoriums and movie halls).
- False ceiling materials are mostly fire-rated and provide fire protection.
Materials for False ceiling
- POP or Plaster of Paris false ceiling
- Gypsum False ceiling
- Metal False ceiling
- Wooden False ceiling
- Mineral fibre board false ceiling
- PVC false ceiling
- Open grid False ceiling
POP of Plaster of Paris False ceiling
Plaster of Paris (POP) is the most popular and economical choice of material for false ceiling works. It is preferred in residential, commercial, and industrial sectors. Plaster of Paris is a white powder obtained by calcinating gypsum. ie. heating at a high temperature to remove the water content.
Steel grids are suspended from the roof and is covered with chicken wire mesh. POP is mixed with water to form a paste. The POP paste is applied over the chicken mesh in layers, leveled, and finished.
POP is a very flexible, durable, and readily available material for false ceilings. It is moulded to any shape, design, and pattern. POP false ceilings are very cheap, elegant, and maintenance-free when compared to other false ceiling materials.
The main disadvantage with POP is the time taken to finish the work. It also creates an enormous amount of wastage. Housekeeping expenses will be high. Plaster of Paris could not match the factory-made superfine surface of gypsum boards. POP is vulnerable to water and moisture and should be avoided for areas prone to water and moisture.
Gypsum board false ceiling
Gypsum board is a premier and widely used surface layer material for interior works. It includes wall, ceiling, and partition systems in residential, institutional, and commercial buildings.
The gypsum panel has a non-combustible gypsum core. It is covered by a firmly bonded specialised paper on the surface and long edges. These panels are fixed on steel frames hanging from the ceiling.
The joints between Gypsum boards are sealed with tapes, thereby giving a seamless and elegant look to the ceiling. Apart from providing a very elegant look, they offer fire resistance and sound control. They are economical, versatile, durable, and very easy to install.
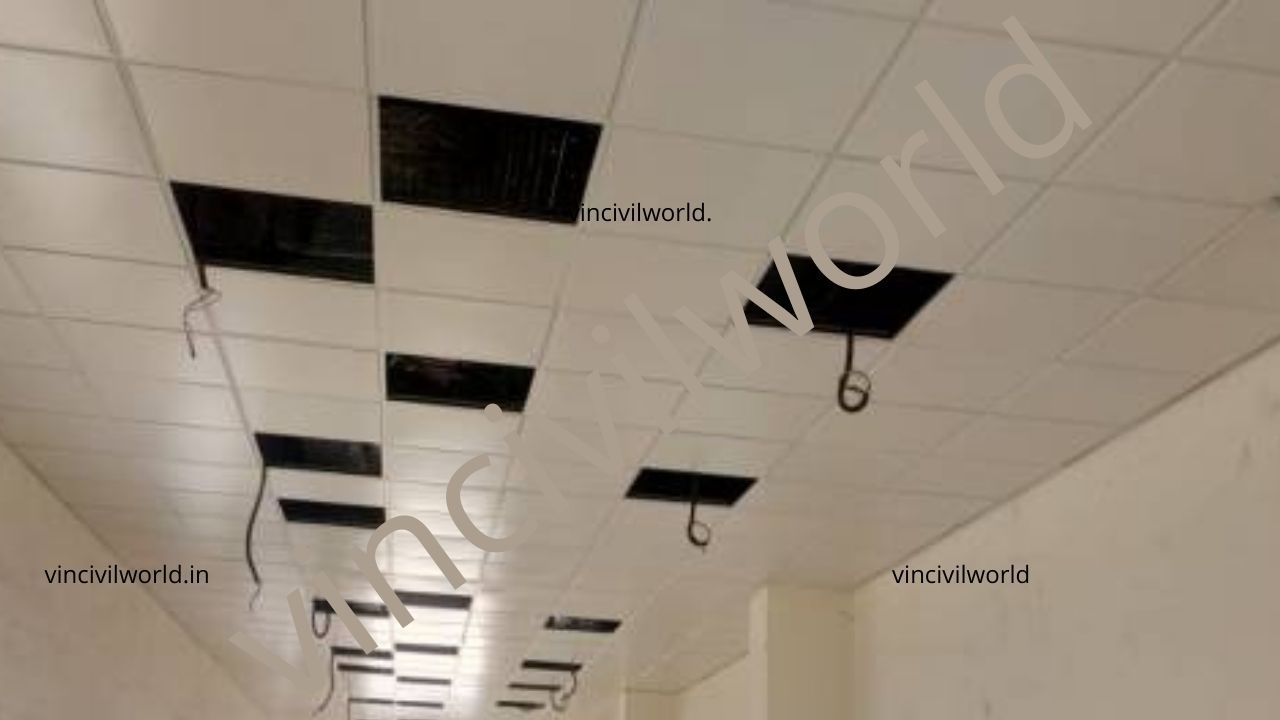
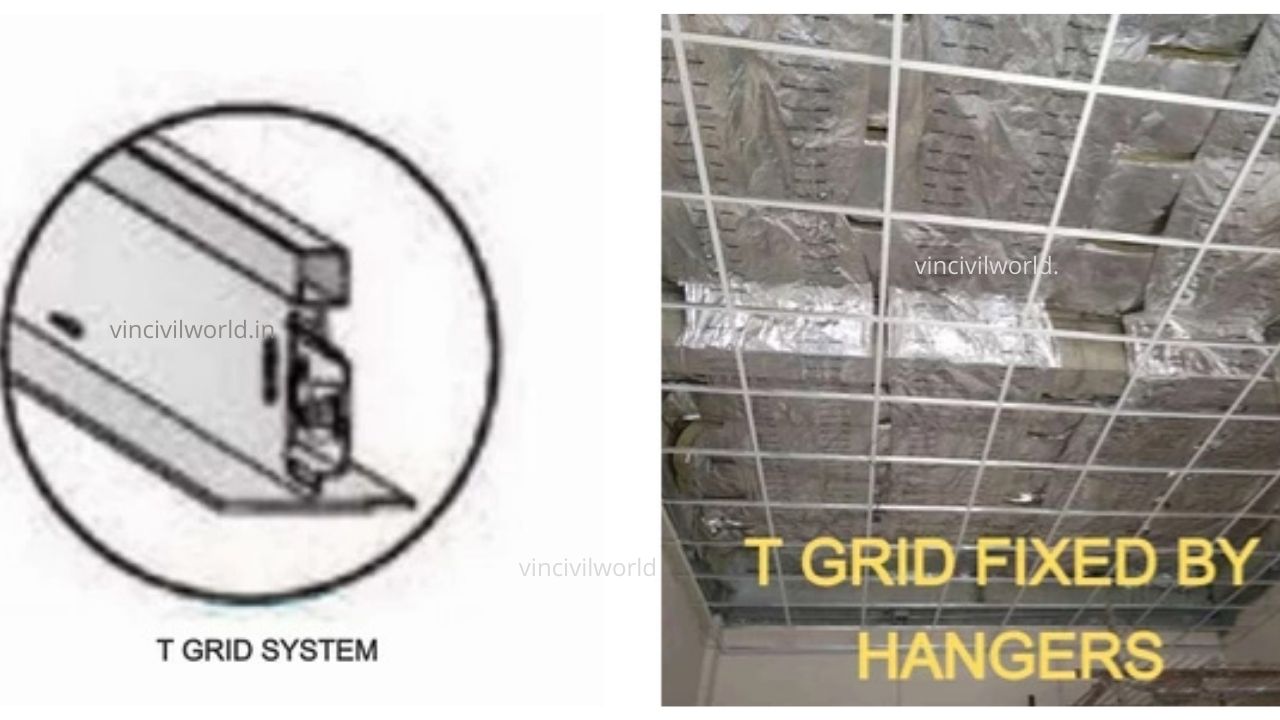
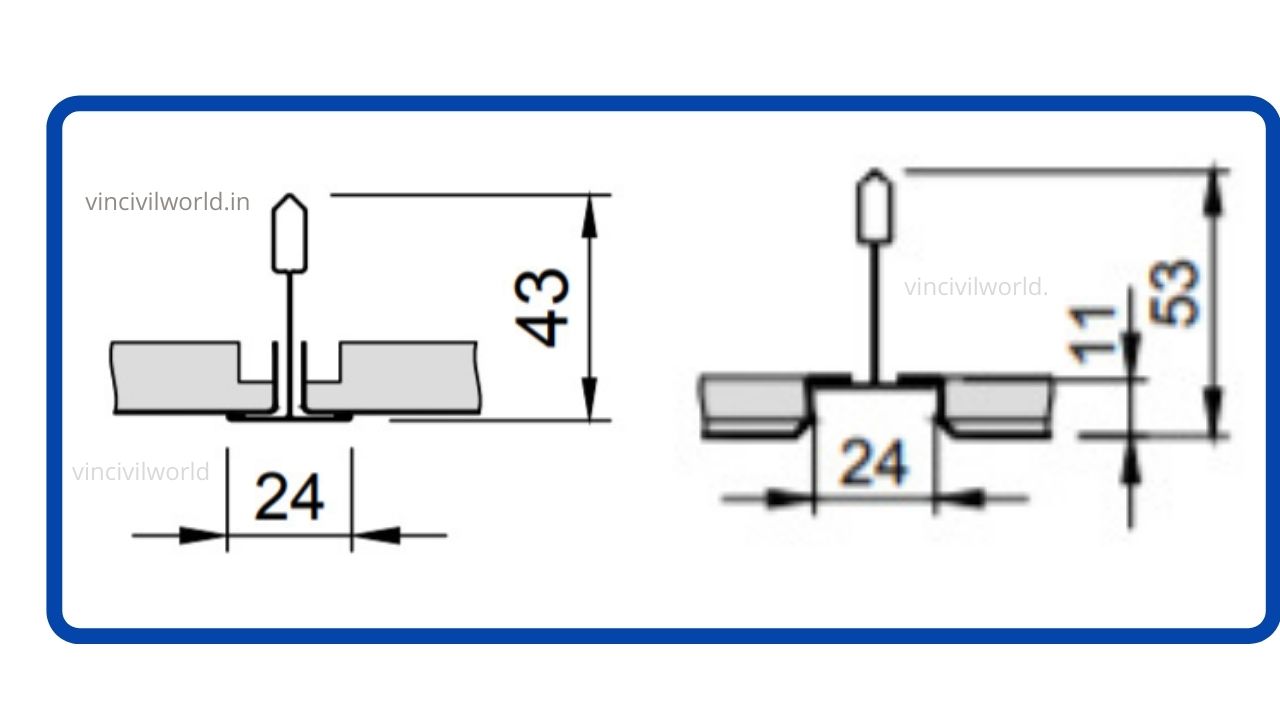
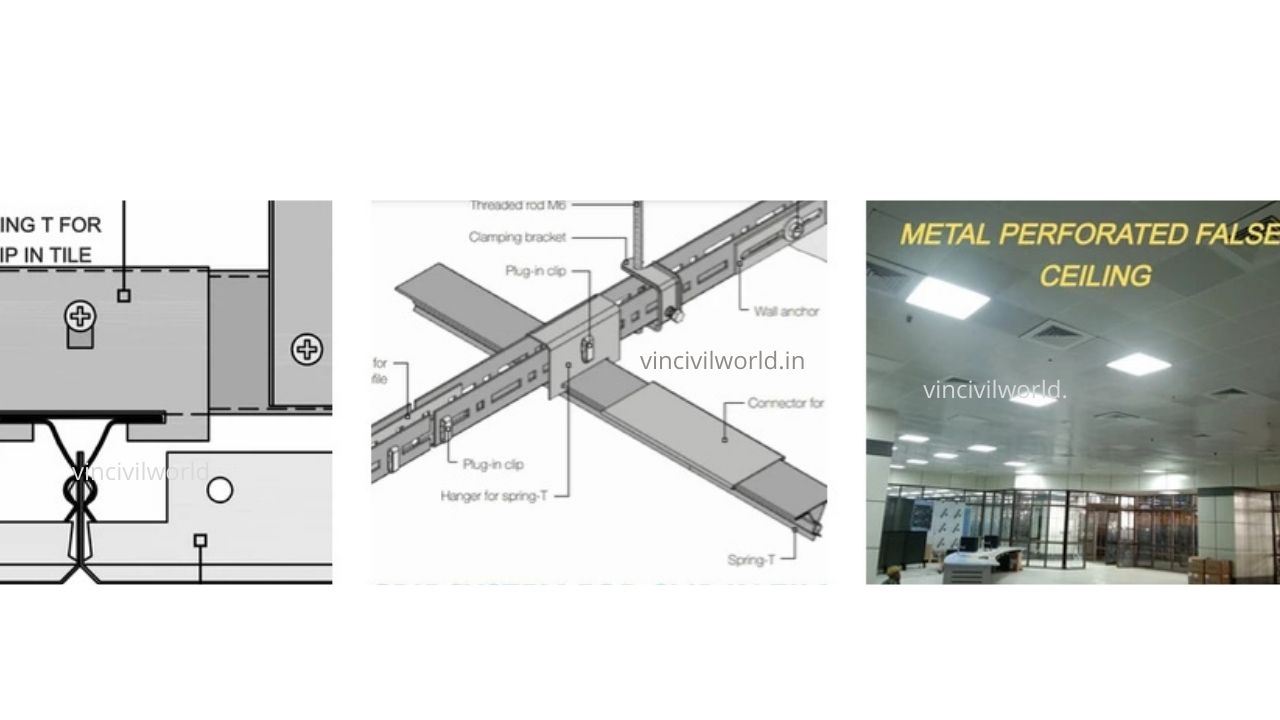
Metal False ceiling (Tile and plant type)
A false ceiling that uses metals either in the form of GALVANISED IRON, STEEL OR ALUMINIUM is called a metal false ceiling. Metal false ceilings are hard, durable and very easy to install. The ceilings are plank type (linear pattern) or grid type. Metal false ceiling tiles are easy to remove and refix after maintenance. They are economical, Maintenance-free and got high self-life when compared to other false ceiling materials.
Metal false ceilings tiles use suspended systems capable of fixing panel and grid tiles.
For more details about the Metal false ceiling please check our earlier article “ Metal false ceiling types – Clip in and Lay in tile.”
Wooden Ceiling
Wooden false ceilings are versatile, classic materials having a variety of natural patterns and textures. They are easy to work with and is installed using screws. Block boards with veneer surfacing are used for wooden false ceiling panels.
Wooden false ceiling is expensive because of its high material cost and higher maintenance cost. They are used in full areas or used as a highlighter. A wooden false ceiling is durable but is vulnerable to termite attacks and moisture.
PVC False Ceiling
PVC or Polyvinyl chloride ceiling is a popular and easy false ceiling option available for residential and commercial areas. PVC false ceiling consists of strong, lightweight, factory-manufactured panels with a hollow core and shiny surface. Polyvinyl chloride false ceilings are strong, seamless finish and come with various designs, colours, sizes and lengths. They are very effective in resisting moisture and water. They are used for bathrooms, balconies, and other areas prone to moisture.
PVC false ceilings are reusable and durable materials that do not require any painting or polishing. They are available in pre-laminated shades and do not split, crack, wrap or rot.
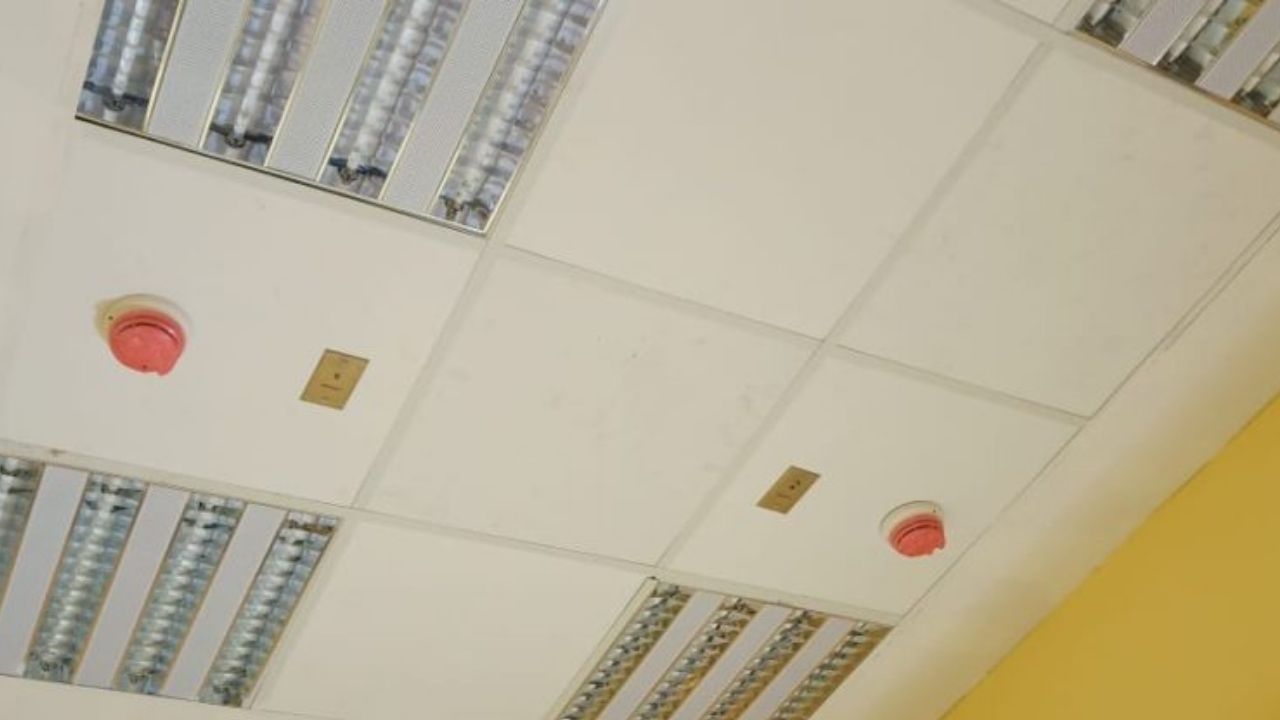
Mineral Fibre Board
Mineral fibre board panels are manufactured using naturally occurring resources to recycled and processed materials. Mineral fibreboard possess excellent acoustic performance and fire resistance properties.
Mineral fibre board false ceiling got a suspended T- Grid Support system like metal false ceilings. They are lightweight and easy to install the environmentally friendly product. The main disadvantage with mineral fibre is that they are brittle and breaks frequently. Mineral fibre boards are vulnerable to water and moisture and painting is not possible over the surface.
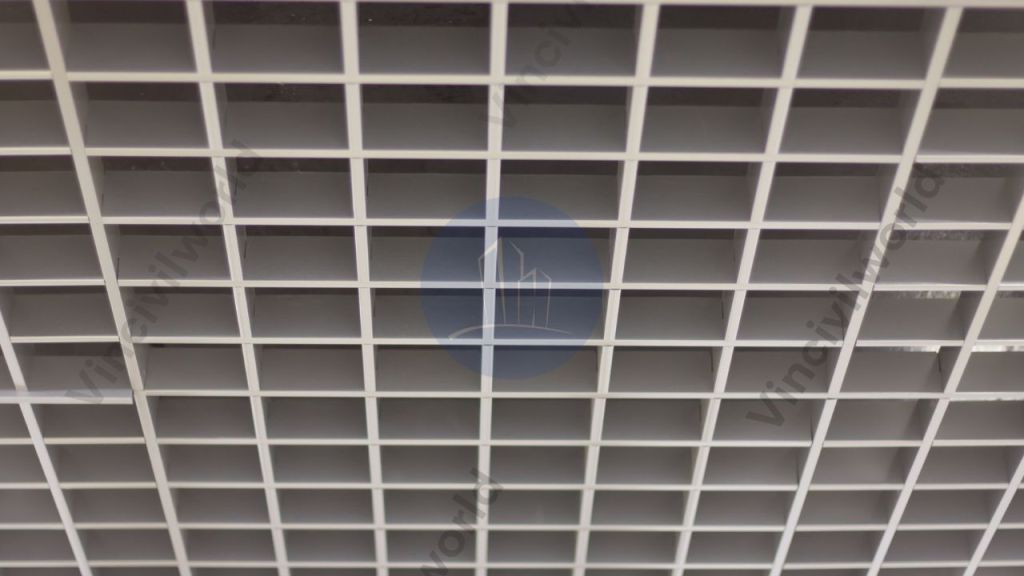
Open Grid False ceilings
Open Cell Ceiling systems comprise a series of open-cell modules designed to lay onto a suspension grid. Open cell ceilings are especially useful for buildings areas lower ceilings without actually changing the roof height.
The tiles are integrated with metal ceiling support systems and plasterboard ceilings. Open cell ceilings are pleasant and can create a visually pleasing look to the room.
Open grid metal ceilings are suitable for the leisure industry, schools, offices, and corporate buildings as well as public spaces.

Disadvantages of false ceiling
- False ceiling reduces the height of the rooms. Hence installation of fans may not be possible.
- Chances of fittings falling from the ceiling.
- Ceilings may sag and de- colourise in course of time and to be replaced.
- Rodents and pests can easily enter the ceiling.
- False ceiling system may fall due to weak supports.
Installation method of all false ceilings
Checks for brickwork
The room’s walls should be perpendicular to each other. Diagonals to be checked to ensure 90 degrees of the walls.
Plastering and painting
- Plastering to be done for a height of 150 mm above the false ceiling.
- The main ceiling and area above the false ceiling are to be rendered.
- A basic coat of primer to be applied before starting ceiling works.
- Final painting to be done after work completion.
Check for concealed systems
- Cabling /wiring relating to all concealed systems like Ceiling lights, Air condition system, Fire alarm and sprinklers, security cameras has to be completed.
- Under deck insulation, if any to be done before doing the ceiling.
- The ducts for supply and return air for the air condition system are to be completed and insulated before starting ceiling works.
Fixing of False ceiling
The ceiling level has to be marked all around the room using marking fluids Edge angle / Wall angle shall be fixed in line with the marking .
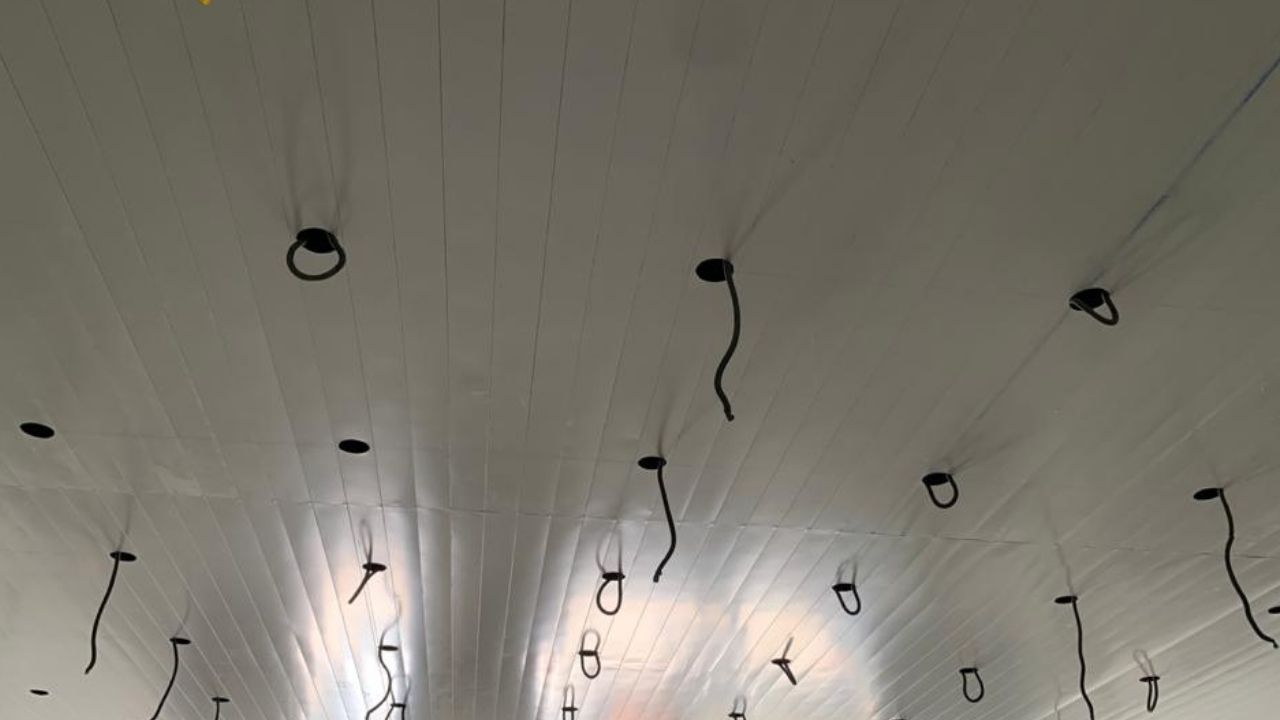
Appropriate hangers (steel wires/steel angles ) in line with the ceiling system shall be fixed to the ceiling using anchor fasteners, likewise the hangers may be used as per the ceiling type and manufacturer. Main grids shall be hanged from the hangers and end of the main grids however should rest on the wall angle. Intermediate tees/ sections are fixed on the main grid for facilitating ceiling boards or tiles fixing.
Cut outs for fixtures
Cut outs required for fixtures shall be done on the board as per drawings, however provision of additional members around the openings to ensure the hold of ceiling fittings.
Precautions For False ceiling works
- Check with the services drawings to ensure completion of concealed wiring works before starting ceiling works.
- Provide strong hangers well enough to handle the false ceiling load.
- The centre portion of the ceiling should be kept little bit higher than the external portion to counter the sagging.
- Light layouts and marking for cut outs should be marked and checked before cutting
- Extra members if required shall be provided in case of cutting of any member coming in line with the fixtures.
- All openings made for cable entry and ducting have to be properly sealed before doing ceiling to restrict pests and rodents from entering the area.